一、GPT 简介
GPT(Generative Pre-trained Transformer)基于 Transformer 解码器自回归地预测下一个 Token,从而进行了语言模型的建模。
只要能够足够好地预测下一个 Token,语言模型便可能具备足够地潜力,从而实现人工智能。
以上就是关于 GPT 和它的能力的一个高层次概述。让我们深入了解更多具体细节。
输入 / 输出
GPT 的函数签名大致如下:
def gpt(inputs: list[int]) -> list[list[float]]: """ GPT代码,实现预测下一个token inputs:List[int], shape为[n_seq],输入文本序列的token id的列表 output:List[List[int]], shape为[n_seq, n_vocab],预测输出的logits列表 """ output = # 需要实现的GPT内部计算逻辑 return output
复制代码
输入
输入是一些由整数表示的文本序列,每个整数都与文本中的 token 一一对应。例如:
text = "robot must obey orders"tokens = ["robot", "must", "obey", "orders"]inputs = [1, 0, 2, 4]
复制代码
token, 即词元,是文本的子片段,使用某种分词器生成。
分词器将文本分割为不可分割的词元单位,实现文本的高效表示,且方便模型学习文本的结构和语义。
分词器对应一个词汇表,我们可用词汇表将 token 映射为整数:
# 词汇表中的token索引表示该token的整数ID# 例如,"robot"的整数ID为1,因为vocab[1] = "robot"vocab = ["must", "robot", "obey", "the", "orders", "."]
# 一个根据空格进行分词的分词器tokenizertokenizer = WhitespaceTokenizer(vocab)
# encode()方法将str字符串转换为list[int]ids = tokenizer.encode("robot must obey orders") # ids = [1, 0, 2, 4]
# 通过词汇表映射,可以看到实际的token是什么tokens = [tokenizer.vocab[i] for i in ids] # tokens = ["robot", "must", "obey", "orders"]
# decode()方法将list[int] 转换回strtext = tokenizer.decode(ids) # text = "robot must obey orders"
复制代码
简而言之:
最后,可以通过 vocab 将 token id 序列再转换回文本。
输出
output 是一个二维数组,其中 output[i][j]表示文本序列的第 i 个位置的 token(inputs[i])是词汇表的第 j 个 token(vocab[j])的概率(实际为未归一化的 logits 得分)。例如:
inputs = [1, 0, 2, 4] # "robot" "must" "obey" "orders"vocab = ["must", "robot", "obey", "the", "orders", "."]output = gpt(inputs)
# output[0] = [0.75, 0.1, 0.15, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]# 给定 "robot",模型预测 "must" 的概率最高
# output[1] = [0.0, 0.0, 0.8, 0.1, 0.0, 0.1]# 给定序列 ["robot", "must"],模型预测 "obey" 的概率最高
# output[-1] = [0.0, 0.0, 0.1, 0.0, 0.85, 0.05]# 给定整个序列["robot", "must", "obey"],模型预测 "orders" 的概率最高next_token_id = np.argmax(output[-1]) # next_token_id = 4next_token = vocab[next_token_id] # next_token = "orders"
复制代码
在上述例子中,输入序列为["robot", "must", "obey"],GPT 模型根据输入,预测序列的下一个 token 是 "output",因为 output[-1][4]的值为 0.85,是词表中最高的一个。
为预测序列的下一个 token,只需在 output 的最后一个位置中选择可能性最高的 token。那么,通过迭代地将上一轮的输出拼接到输入,并送入模型,从而持续地生成 token。
这种生成方式称为贪心采样。实际可以对类别分布用温度系数 T 进行蒸馏(放大或减小分布的不确定性),并截断类别分布的按 top-k,再进行类别分布采样。
具体地,在每次迭代中,将上一轮预测出的 token 添加到输入末尾,然后预测下一个位置的值,如此往复,就是整个自回归的预测过程:
def generate(inputs, n_tokens_to_generate): """ GPT生成代码 inputs: list[int], 输入文本的token ids列表 n_tokens_to_generate:int, 需要生成的token数量 """ # 自回归式解码循环 for _ in range(n_tokens_to_generate): output = gpt(inputs) # 模型前向推理,输出预测词表大小的logits列表 next_id = np.argmax(output[-1]) # 贪心采样 inputs.append(int(next_id)) # 将预测添加回输入 return inputs[len(inputs) - n_tokens_to_generate :] # 只返回生成的ids
# 随便举例input_ids = [1, 0, 2] # ["robot", "must", "obey"]output_ids = generate(input_ids, 1) # output_ids = [1, 0, 2, 4]output_tokens = [vocab[i] for i in output_ids] # ["robot", "must", "obey", "orders"]
复制代码
二、GPT 结构与实现
2.1 基本组成部分
首先,导入相关可视化函数
import randomimport numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def plot(x, y, x_axis=None, y_axis=None): plt.plot(x, y) if x_axis and isinstance(x_axis, tuple): plt.xlim(x_axis[0], x_axis[1]) if y_axis and isinstance(y_axis, tuple): plt.ylim(y_axis[0], y_axis[1]) plt.show()
def plotHot(w): plt.figure() plt.imshow(w, cmap='hot', interpolation='nearest') plt.show()
复制代码
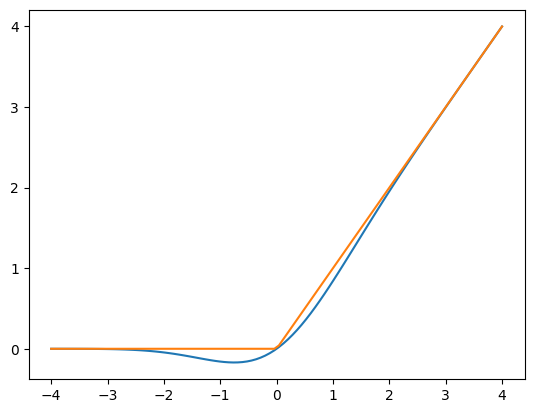
GELU
GPT-2 选择的 FFN 中的非线性激活函数是 GELU(高斯误差线性单元),是 ReLU 的对比的一种替代方法。它由以下函数近似表示:
def gelu(x): return 0.5 * x * (1 + np.tanh(np.sqrt(2 / np.pi) * (x + 0.044715 * x**3)))
def relu(x): return np.maximum(0, x)
复制代码
GELU 与 ReLU 的对比
print(gelu(np.array([1, 2, -2, 0.5])))print(relu(np.array([1, 2, -2, 0.5])))
x = np.linspace(-4, 4, 100) plot(x, np.array([gelu(x), relu(x)]).transpose())
复制代码
Softmax
原始 Softmax 公式:
相比原始 Softmax, 这里使用了减去最大值 max(x)技巧来保持数值稳定性。
def softmax(x): # 减去最大值,避免溢出,不影响分布 exp_x = np.exp(x - np.max(x, axis=-1, keepdims=True)) return exp_x / np.sum(exp_x, axis=-1, keepdims=True)
def rawSoftmax(x): exp_x = np.exp(x) return exp_x / np.sum(exp_x)
复制代码
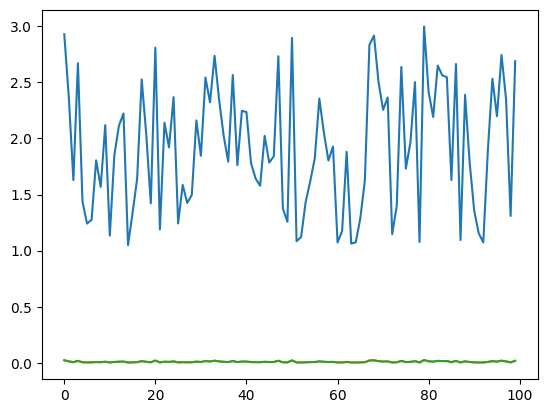
num = 100 # 生成不重复的随机数,比较 原始值、原始softmax和修正后的softmaxnumbers = []for i in range(num): number = random.uniform(1, 3) while number in numbers: number = random.uniform(1, 3) numbers.append(number)plot(np.array(range(num)), np.array([numbers, rawSoftmax(numbers), softmax(numbers)]).transpose())
复制代码
在输入在合理范围时,两者输出基本相同。
raw_x = np.array([[-200, 100, -300, 0, 70000000]])x1 = softmax(raw_x)x2 = rawSoftmax(np.array(raw_x))print(x1, x1.sum(axis=-1), softmax(x1))print(x2, x2.sum(axis=-1), softmax(x2))
复制代码
在输入存在异常值时,输出结果比较(原始 softmax 出现 nan)
[[0. 0. 0. 0. 1.]] [1.] [[0.14884758 0.14884758 0.14884758 0.14884758 0.40460968]][[ 0. 0. 0. 0. nan]] [nan] [[nan nan nan nan nan]]tmp.py:7: RuntimeWarning: overflow encountered in exp exp_x = np.exp(x)tmp.py:8: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in divide return exp_x / np.sum(exp_x)
复制代码
层归一化
层归一化(Layer Normalization)是基于特征维度将数据进行标准化(均值为 0 方差为 1),同时乘以缩放系数、加上平移系数,保留其非线性能力:
层归一化可以有效地缓解优化过程中潜在的不稳定、收敛速度慢等问题。
def layer_norm(x, g, b, eps: float = 1e-5): """ 层归一化操作 x: np.array, 输入 g: float, 可学习的缩放参数 gamma b: float, 可学习的平移参数 beta eps: float, 避免方差为0从而除零的极小值 """ mean = np.mean(x, axis=-1, keepdims=True) variance = np.var(x, axis=-1, keepdims=True) x = (x - mean) / np.sqrt(variance + eps) # 将x沿着最后一个轴,进行标准化 return g * x + b # 将标准化后的x进行重新缩放和平移
复制代码
可视化例子
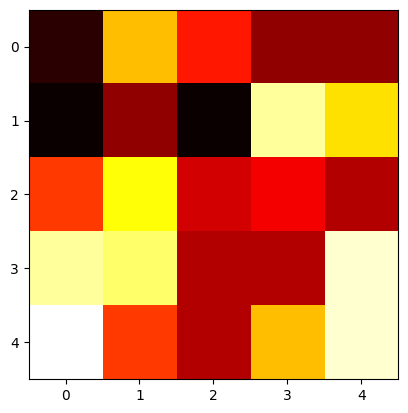
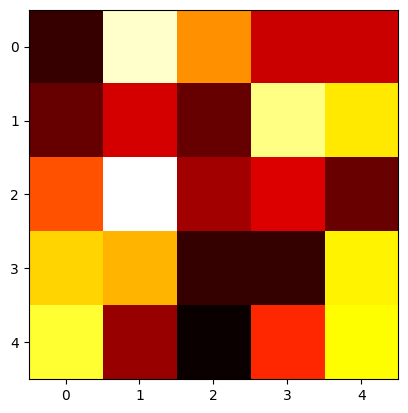
num, dim = 5, 5x = np.array([[random.randint(-10, 10) for _ in range(dim)] for _ in range(num)] )g, b = 1, 0 # 不缩放和平移x_norm = layer_norm(x, g, b)print(x)print(x_norm)plotHot(x)plotHot(x_norm)
复制代码
输出结果
# 层归一化前[[ -9 3 -2 -6 -6] [-10 -6 -10 8 4] [ -1 5 -4 -3 -5] [ 8 7 -5 -5 9] [ 10 -1 -5 3 9]] # 层归一化后[[-1.2056067 1.68784939 0.48224268 -0.48224268 -0.48224268] [-0.96768591 -0.43008263 -0.96768591 1.45152886 0.91392558] [ 0.16876312 1.8563943 -0.67505247 -0.39378061 -0.95632434] [ 0.8124999 0.65624992 -1.21874985 -1.21874985 0.96874988] [ 1.18444594 -0.73156955 -1.42830246 -0.03483665 1.01026272]]
复制代码
层归一化前
层归一化后(每行数据经过标准化后,分布差异变小了,从而输入网络的数据的分布得到了限制)
通过折线图可视化(每条折线代表一个行向量),可以更明显地看到变化:
axis = np.array(range(x.shape[0]))plot(axis, x)plot(axis, x_norm)
复制代码
层归一化前
层归一化后
线性(仿射变换)层
标准的矩阵乘法+偏置:
def linear(x, w, b): # [m, in], [in, out], [out] -> [m, out] return x @ w + b
复制代码
例子
n_num = 3in_dim, hid_dim = 4, 4x = np.random.normal(size=(n_num, in_dim))w = np.random.normal(size=(in_dim, hid_dim))b = np.random.normal(size=(hid_dim,))h = linear(x, w, b)print(f"shape of w: {w.shape}")print(f"input shape: {x.shape}, output shape: {h.shape}")plotHot(w)
复制代码
shape of w: (4, 4)input shape: (3, 4), output shape: (3, 4)权重可视化
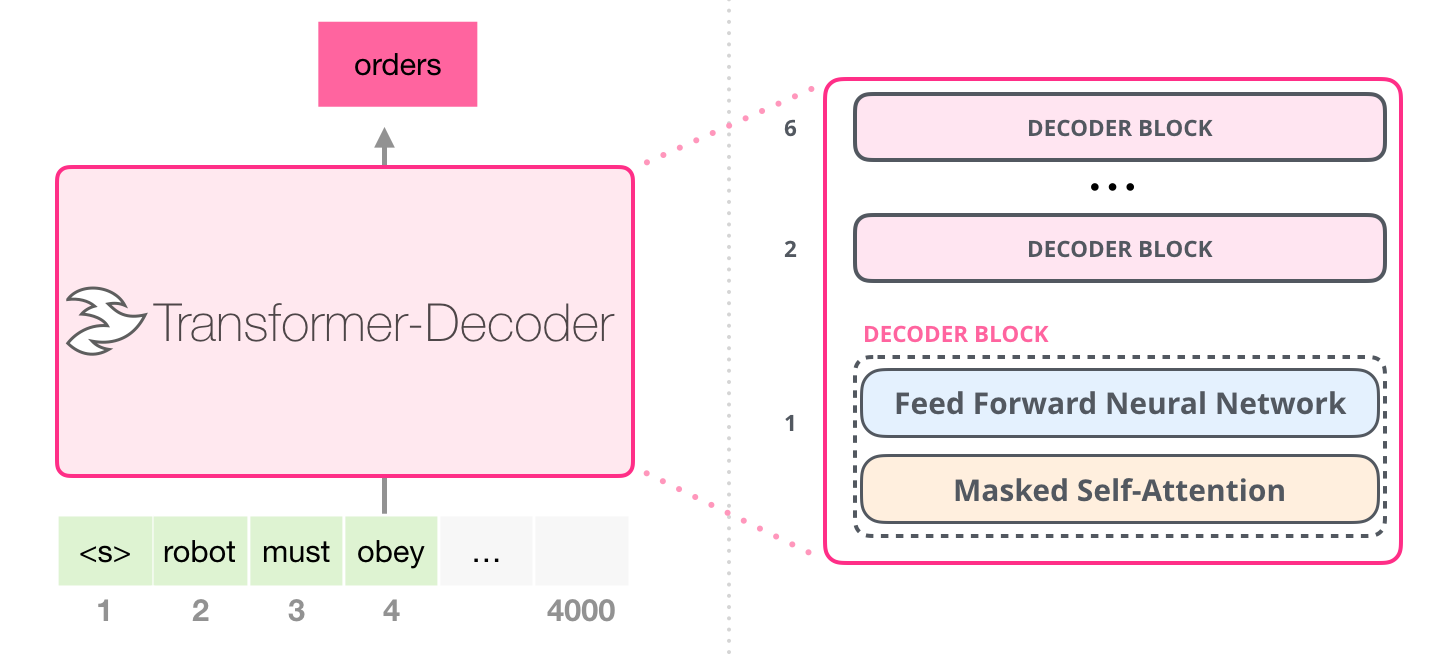
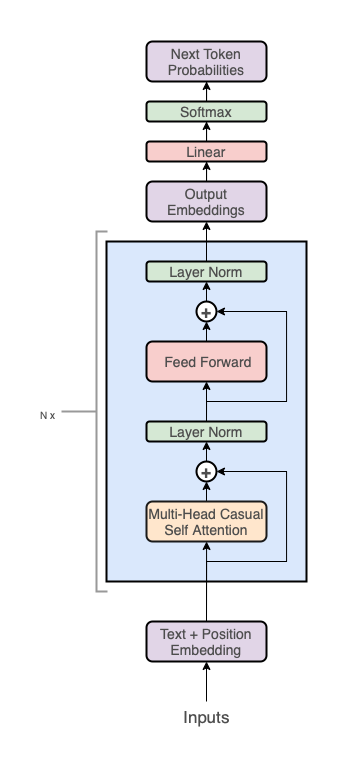
2.2 GPT 架构
从整体上来看,GPT 架构分为三个部分:
代码层 GPT 实现
def gpt2(inputs, wte, wpe, blocks, ln_f, n_head): """ GPT2模型实现 输入输出tensor形状: [n_seq] -> [n_seq, n_vocab] n_vocab, 词表大小 n_seq, 输入token序列长度 n_layer, 自注意力编码器的层数 n_embd, 词表的词元嵌入大小 n_ctx, 输入最大序列长度(位置编码支持的长度,可用ROPE旋转位置编码提升外推长度) params: inputs: List[int], token ids, 输入token ids wte: np.ndarray[n_vocab, n_embd], token嵌入矩阵 (与输出分类器共享参数) wpe: np.ndarray[n_ctx, n_embd], 位置编码嵌入矩阵 blocks:object, n_layer层因果自注意力编码器 ln_f:tuple[float], 层归一化参数 n_head:int, 注意力头数 """ # 1、在词元嵌入中添加位置编码信息:token + positional embeddings x = wte[inputs] + wpe[range(len(inputs))] # [n_seq] -> [n_seq, n_embd]
# 2、前向传播n_layer层Transformer blocks for block in blocks: x = transformer_block(x, **block, n_head=n_head) # [n_seq, n_embd] -> [n_seq, n_embd]
# 3、Transformer编码器块的输出投影到词汇表概率分布上 # 预测下个词在词表上的概率分布[ 输出语言模型的建模的条件概率分布p(x_t|x_t-1 ... x_1) ] x = layer_norm(x, **ln_f) # [n_seq, n_embd] -> [n_seq, n_embd] # 就是和嵌入矩阵进行内积(编码器块的输出相当于预测值,内积相当于求相似度最大的词汇) return x @ wte.T # [n_seq, n_embd] -> [n_seq, n_vocab]
复制代码
嵌入表示层
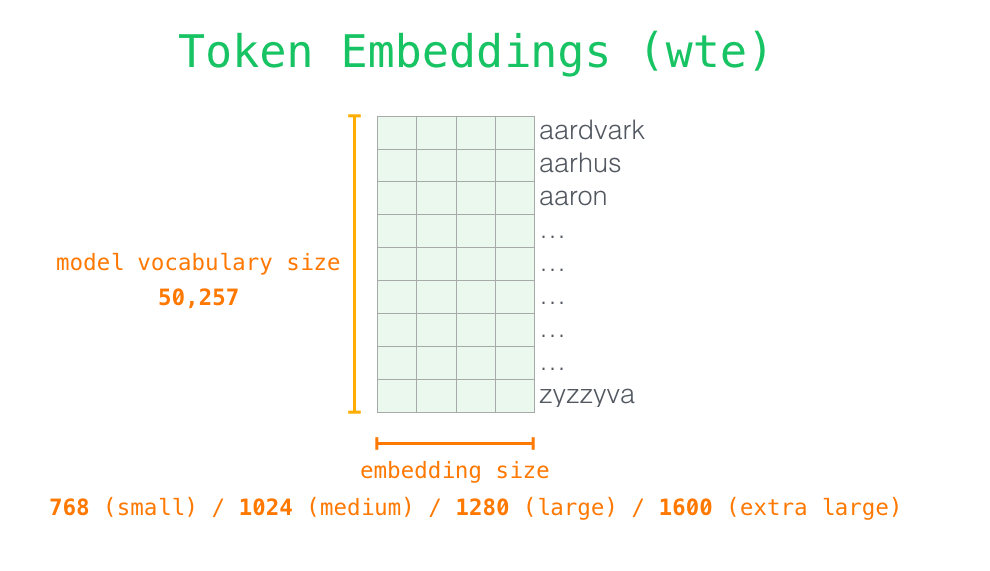
Token embeddingswte 是一个[n_vocab, n_embd]可学习参数矩阵,它充当一个 token 嵌入查找表,其中矩阵的第 i�行对应于我们词汇表中第 i�个 token 的 embedding。wte[inputs] 使用整数数组索引来检索与输入中每个 token 对应的向量。
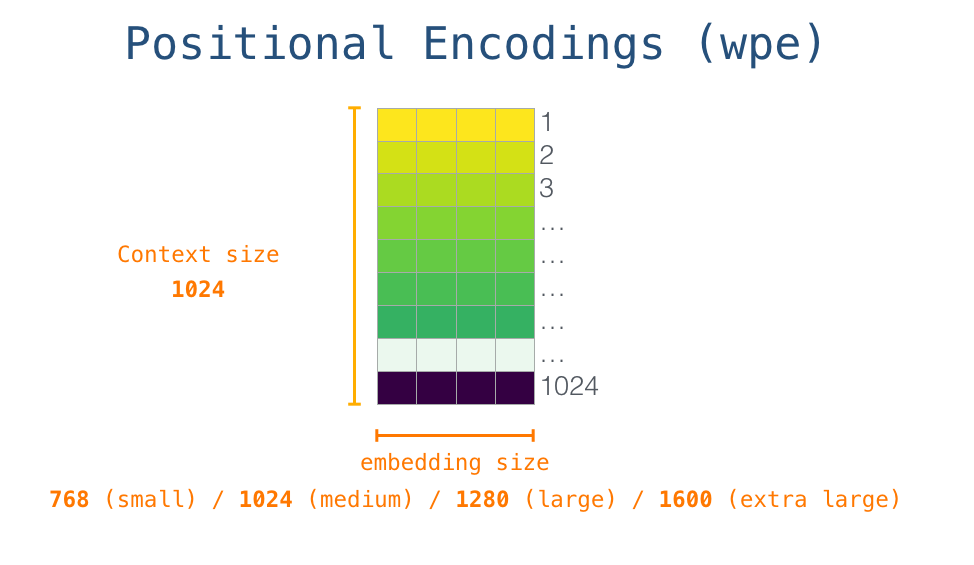
Positional embeddings 为了编码序列的顺序信息,通过在输入表示中添加位置编码(positional encoding)嵌入来注入位置信息。位置编码可以通过学习得到也可以直接固定得到。
大小为[n_ctx, n_embd]的 wpe 即可学习的位置嵌入矩阵,其中矩阵的第 i�行对应输入序列中第 i�个 token 的位置 embedding,编码了对应的位置信息。
n_ctx 代表最大序列长度,限制了模型外推的最大范围。n_ctx 代表最大序列长度,限制了模型外推的最大范围。
在 GPT 中,位置嵌入矩阵 wpe 和 token embeddings 类似,先随机初始化,后通过训练学习得到。wpe[inputs] 使用整数数组索引 inputs 来检索与输入中每个 token 对应的位置嵌入。
将 token 嵌入与位置嵌入联合为一个组合嵌入,这个嵌入将 token 信息和位置信息都编码进来了。
Token + Positional embeddings 将 Tokene mbeddings 与位置嵌入拼接后的嵌入,将 token 信息和位置信息都编码进来了,它将作为 transoformer decoder blocks 的实际输入。
x = wte[inputs] + wpe[range(len(inputs))] # [n_seq] -> [n_seq, n_embd]
复制代码
解码层
transformer 解码器模块由两个子层组成:
transformer 解码器中,堆叠了 num_layers 个如下的 transformer_block:
def transformer_block(x, mlp, attn, ln_1, ln_2, n_head): """ 自注意力编码器层实现 (只实现逻辑,各个子模块参数需传入) 输入输出tensor形状: [n_seq, n_embd] -> [n_seq, n_embd] n_seq, 输入token序列长度 n_embd, 词表的词元嵌入大小 params: x: np.ndarray[n_seq, n_embd], 输入token嵌入序列 mlp: object, 前馈神经网络 attn: object, 注意力编码器层 ln1: object, 线性层1 ln2: object, 线性层2 n_head:int, 注意力头数 """ # Multi-head Causal Self-Attention (层归一化 + 多头自注意力 + 残差连接 ) x = x + mha(layer_norm(x, **ln_1), **attn, n_head=n_head) # [n_seq, n_embd] -> [n_seq, n_embd]
# Position-wise Feed Forward Network x = x + ffn(layer_norm(x, **ln_2), **mlp) # [n_seq, n_embd] -> [n_seq, n_embd]
return x
复制代码
Self-Attention 中的层规一化和残差连接用于提升训练的稳定性。
残差连接残差连接引入输入直接到输出的通路,便于梯度回传从而缓解在优化过程中由于网络过深引起的梯度消失问题。
位置感知的前馈网络对序列中的所有位置的表示进行变换时使用的是同一个 2 层隐藏层的 MLP,故称其为 position-wise 的前馈网络(Position-wise Feed Forward Network)。
def ffn(x, c_fc, c_proj): """ 2层前馈神经网络实现 (只实现逻辑,各个子模块参数需传入) 输入输出tensor形状: [n_seq, n_embd] -> [n_seq, n_embd] n_seq, 输入token序列长度 n_embd, 词表的词元嵌入大小 n_hid, 隐藏维度 params: x: np.ndarray[n_seq, n_embd], 输入token嵌入序列 c_fc: np.ndarray[n_embd, n_hid], 升维投影层参数, 默认:4*n_embd c_proj: np.ndarray[n_hid, n_embd], 降维投影层参数 """ # project up:将n_embd投影到一个更高的维度 4*n_embd a = gelu(linear(x, **c_fc)) # [n_seq, n_embd] -> [n_seq, 4*n_embd]
# project back down:投影回n_embd x = linear(a, **c_proj) # [n_seq, 4*n_embd] -> [n_seq, n_embd]
return x
复制代码
这里仅仅是升维再降维,具体地将 n_embd 投影到一个更高的维度 4*n_embd,然后再将其投影回 n_embd。
多头因果自注意力这里将通过分别解释“多头因果自注意力”的每个词,来一步步理解“多头因果自注意力”:
缩放点积注意力(scaled dot-product attention)
def attention_raw(q, k, v): """ 原始缩放点积注意力实现 输入输出tensor形状: [n_q, d_k], [n_k, d_k], [n_k, d_v] -> [n_q, d_v] params: q: np.ndarray[n_seq, n_embd], 查询向量 k: np.ndarray[n_seq, n_embd], 键向量 v: np.ndarray[n_seq, n_embd], 值向量 """ return softmax(q @ k.T / np.sqrt(q.shape[-1])) @ v
# 以通过对q、k、v进行投影变换来增强自注意效果def self_attention_raw(x, w_k, w_q, w_v, w_proj): """ 自注意力原始实现 输入输出tensor形状: [n_seq, n_embd] -> [n_seq, n_embd] params: x: np.ndarray[n_seq, n_embd], 输入token嵌入序列 w_k: np.ndarray[n_embd, n_embd], 查询向量投影层参数 w_q: np.ndarray[n_embd, n_embd], 键向量投影层参数 w_v: np.ndarray[n_embd, n_embd], 值向量投影层参数 w_proj: np.ndarray[n_embd, n_embd], 自注意力输出投影层参数 """ # qkv projections q = x @ w_k # [n_seq, n_embd] @ [n_embd, n_embd] -> [n_seq, n_embd] k = x @ w_q # [n_seq, n_embd] @ [n_embd, n_embd] -> [n_seq, n_embd] v = x @ w_v # [n_seq, n_embd] @ [n_embd, n_embd] -> [n_seq, n_embd]
# perform self attention x = attention(q, k, v) # [n_seq, n_embd] -> [n_seq, n_embd]
# out projection x = x @ w_proj # [n_seq, n_embd] @ [n_embd, n_embd] -> [n_seq, n_embd]
return x
# 将w_q、w_k和w_v组合成一个单独的矩阵w_fc,执行投影操作,然后拆分结果,我们就可以将矩阵乘法的数量从4个减少到2个def self_attention(x, c_attn, c_proj): """ 自注意力优化后实现(w_q 、w_k 、w_v合并成一个矩阵w_fc进行投影,再拆分结果) 同时GPT-2的实现:加入偏置项参数(所以使用线性层,进行仿射变换) 输入输出tensor形状: [n_seq, n_embd] -> [n_seq, n_embd] params: x: np.ndarray[n_seq, n_embd], 输入token嵌入序列 w_fc: np.ndarray[n_embd, 3*n_embd], 查询向量投影层参数 w_proj: np.ndarray[n_embd, n_embd], 自注意力输出投影层参数 """ # qkv projections x = linear(x, **c_attn) # [n_seq, n_embd] -> [n_seq, 3*n_embd]
# split into qkv q, k, v = np.split(x, 3, axis=-1) # [n_seq, 3*n_embd] -> 3 of [n_seq, n_embd]
# perform self attention x = attention(q, k, v) # [n_seq, n_embd] -> [n_seq, n_embd]
# out projection x = linear(x, **c_proj) # [n_seq, n_embd] @ [n_embd, n_embd] = [n_seq, n_embd]
return x
复制代码
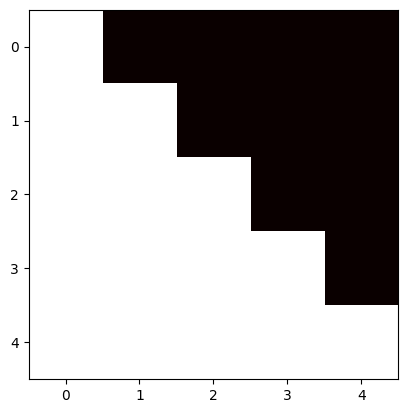
因果
为了防止序列建模时出现信息泄露,需要修改注意力矩阵(增加 Mask)以隐藏或屏蔽我们的输入,从而避免模型在训练阶段直接看到后续的文本序列(信息泄露)进而无法得到有效地训练。
# 输入是 ["not", "all", "heroes", "wear", "capes"]
# 原始自注意力 not all heroes wear capes not 0.116 0.159 0.055 0.226 0.443 all 0.180 0.397 0.142 0.106 0.175heroes 0.156 0.453 0.028 0.129 0.234 wear 0.499 0.055 0.133 0.017 0.295 capes 0.089 0.290 0.240 0.228 0.153
# 因果自注意力 (行为j, 列为i) # 为防止输入的所有查询都能预测未来,需要将所有j>i位置设置为0 : not all heroes wear capes not 0.116 0. 0. 0. 0. all 0.180 0.397 0. 0. 0.heroes 0.156 0.453 0.028 0. 0. wear 0.499 0.055 0.133 0.017 0. capes 0.089 0.290 0.240 0.228 0.153
# 在应用 softmax 之前,我们需要修改我们的注意力矩阵,得到掩码自注意力 # 即,在softmax之前将要屏蔽项的注意力得分设置为 −∞(归一化系数为0) # mask掩码矩阵 0 -1e10 -1e10 -1e10 -1e10 0 0 -1e10 -1e10 -1e10 0 0 0 -1e10 -1e10 0 0 0 0 -1e10 0 0 0 0 0
使用 -1e10 而不是 -np.inf ,因为 -np.inf 可能会导致 nans
复制代码
加入掩码矩阵的注意力实现:
def attention(q, k, v, mask): """ 缩放点积注意力实现 输入输出tensor形状: [n_q, d_k], [n_k, d_k], [n_k, d_v] -> [n_q, d_v] params: q: np.ndarray[n_seq, n_embd], 查询向量 k: np.ndarray[n_seq, n_embd], 键向量 v: np.ndarray[n_seq, n_embd], 值向量 mask: np.ndarray[n_seq, n_seq], 注意力掩码矩阵 """ return softmax(q @ k.T / np.sqrt(q.shape[-1]) + mask) @ v
复制代码
因果注意力掩码矩阵可视化
x = np.array([1, 1, 1, 1, 1])causal_mask = (1 - np.tri(x.shape[0], dtype=x.dtype))* -1e10 print(causal_mask)plotHot(causal_mask)
复制代码
[[-0.e+00 -1.e+10 -1.e+10 -1.e+10 -1.e+10] [-0.e+00 -0.e+00 -1.e+10 -1.e+10 -1.e+10] [-0.e+00 -0.e+00 -0.e+00 -1.e+10 -1.e+10] [-0.e+00 -0.e+00 -0.e+00 -0.e+00 -1.e+10] [-0.e+00 -0.e+00 -0.e+00 -0.e+00 -0.e+00]]
复制代码
注意力可视化
def causal_self_attention(x, c_attn, c_proj): """ 因果自注意力优化后实现(w_q 、w_k 、w_v合并成一个矩阵w_fc进行投影,再拆分结果) 同时GPT-2的实现:加入偏置项参数(所以使用线性层,进行仿射变换) 输入输出tensor形状: [n_seq, n_embd] -> [n_seq, n_embd] params: x: np.ndarray[n_seq, n_embd], 输入token嵌入序列 c_attn: np.ndarray[n_embd, 3*n_embd], 查询向量投影层参数 c_proj: np.ndarray[n_embd, n_embd], 自注意力输出投影层参数 """ # qkv projections x = linear(x, **c_attn) # [n_seq, n_embd] -> [n_seq, 3*n_embd]
# split into qkv q, k, v = np.split(x, 3, axis=-1) # [n_seq, 3*n_embd] -> 3 of [n_seq, n_embd]
# causal mask to hide future inputs from being attended to causal_mask = (1 - np.tri(x.shape[0], dtype=x.dtype))* -1e10 # [n_seq, n_seq]
# perform causal self attention x = attention(q, k, v, causal_mask) # [n_seq, n_embd] -> [n_seq, n_embd]
# out projection x = linear(x, **c_proj) # [n_seq, n_embd] @ [n_embd, n_embd] = [n_seq, n_embd]
return x
复制代码
实际,用-1e10 替换-np.inf, 因为-np.inf 会导致 nans 错误。
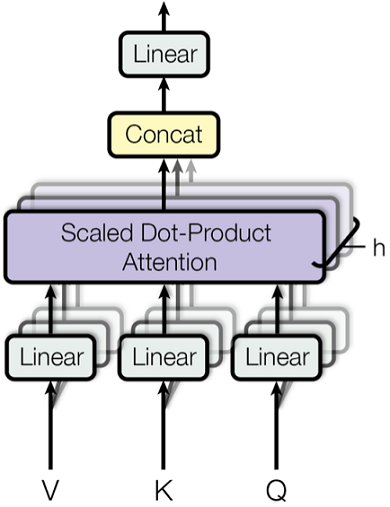
多头自注意力(Multi-Head-self-Attention)
def mha(x, c_attn, c_proj, n_head): """ 多头自注意力实现 输入输出tensor形状: [n_seq, n_embd] -> [n_seq, n_embd] 每个注意力计算的维度从n_embd降低到 n_embd/n_head。 通过降低维度,模型利用多个子空间进行建模 params: x: np.ndarray[n_seq, n_embd], 输入token嵌入序列 c_attn: np.ndarray[n_embd, 3*n_embd], 查询向量投影层参数 c_proj: np.ndarray[n_embd, n_embd], 自注意力输出投影层参数 """ # qkv投影变换 x = linear(x, **c_attn) # [n_seq, n_embd] -> [n_seq, 3*n_embd]
# 划分为qkv qkv = np.split(x, 3, axis=-1) # [n_seq, 3*n_embd] -> [3, n_seq, n_embd]
# 将n_embd继续划分为_head个注意力头 qkv_heads = list(map(lambda x: np.split(x, n_head, axis=-1), qkv)) # [3, n_seq, n_embd] -> [3, n_head, n_seq, n_embd/n_head]
# 构造causal mask矩阵 causal_mask = (1 - np.tri(x.shape[0], dtype=x.dtype))* -1e10 # [n_seq, n_seq]
# 单独执行每个头的因果自注意力(可多核多线程并行执行) out_heads = [attention(q, k, v, causal_mask) for q, k, v in zip(*qkv_heads)] # [3, n_head, n_seq, n_embd/n_head] -> [n_head, n_seq, n_embd/n_head]
# 合并多个heads的结果 x = np.hstack(out_heads) # [n_head, n_seq, n_embd/n_head] -> [n_seq, n_embd]
# 多头因果自注意力输出projection x = linear(x, **c_proj) # [n_seq, n_embd] -> [n_seq, n_embd]
return x
复制代码
将所有代码组合起来将所有代码组合起来就得到了 gpt2.py,总共的代码只有 120 行(如果你移除注释、空格之类的,那就只有 60 行)。
二、项目实战
可以通过以下代码测试:
python gpt2.py "Alan Turing theorized that computers would one day become" --n_tokens_to_generate 8
复制代码
其输出是:the most powerful machines on the planet.
ToDO
文章转载自:LeonYi
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/justLittleStar/p/17925108.html
体验地址:http://www.jnpfsoft.com/?from=001
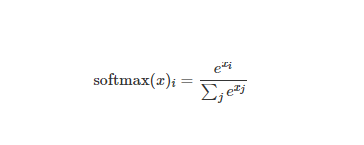
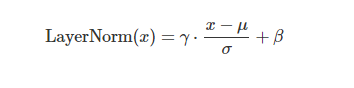

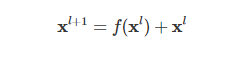
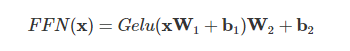
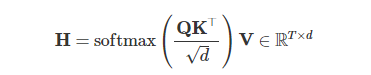
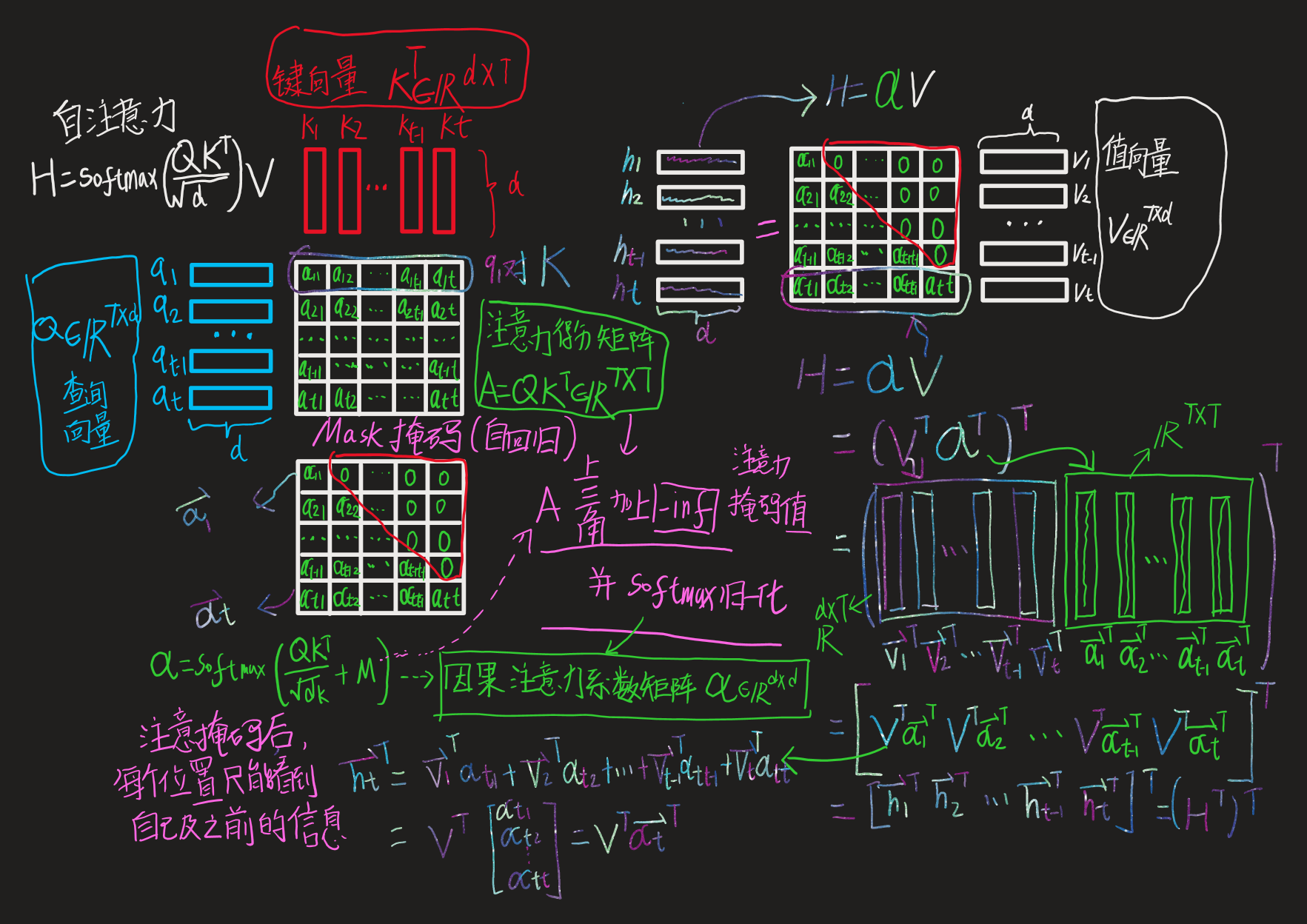








评论