AOP 中动态代理详解
- 2024-12-23 福建
本文字数:16947 字
阅读完需:约 56 分钟
动态代理概述
什么是代理
代理模式(Proxy pattern): 为另一个对象提供一个替身或占位符以控制对这个对象的访问
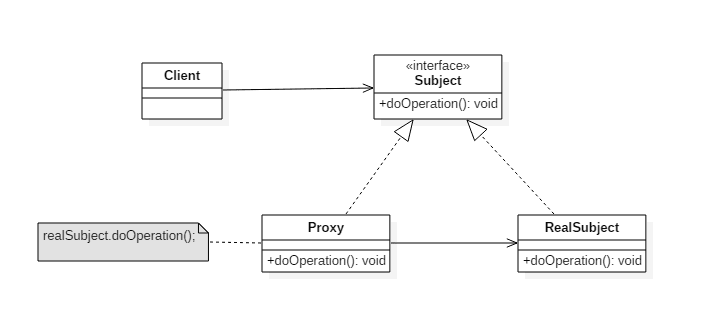
什么是动态代理?
动态代理就是,在程序运行期,创建目标对象的代理对象,并对目标对象中的方法进行功能性增强的一种技术。
在生成代理对象的过程中,目标对象不变,代理对象中的方法是目标对象方法的增强方法。可以理解为运行期间,对象中方法的动态拦截,在拦截方法的前后执行功能操作。
代理的创建
创建代理的方法是 postProcessAfterInitialization:如果 bean 被子类标识为代理,则使用配置的拦截器创建一个代理
/** * Create a proxy with the configured interceptors if the bean is * identified as one to proxy by the subclass. * @see #getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean */@Overridepublic Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) { if (bean != null) { Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName); // 如果不是提前暴露的代理 if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) { return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey); } } return bean;}wrapIfNecessary 方法主要用于判断是否需要创建代理,如果 Bean 能够获取到 advisor 才需要创建代理
/** * Wrap the given bean if necessary, i.e. if it is eligible for being proxied. * @param bean the raw bean instance * @param beanName the name of the bean * @param cacheKey the cache key for metadata access * @return a proxy wrapping the bean, or the raw bean instance as-is */protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) { // 如果bean是通过TargetSource接口获取 if (beanName != null && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) { return bean; } // 如果bean是切面类 if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) { return bean; } // 如果是aop基础类?是否跳过? if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) { this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; }
// 重点:获取所有advisor,如果没有获取到,那说明不要进行增强,也就不需要代理了。 Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null); if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) { this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE); // 重点:创建代理 Object proxy = createProxy( bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean)); this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass()); return proxy; }
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean;}获取所有的 Advisor
我们看下获取所有 advisor 的方法 getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean
@Override@Nullableprotected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean( Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, @Nullable TargetSource targetSource) {
List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName); if (advisors.isEmpty()) { return DO_NOT_PROXY; } return advisors.toArray();}通过 findEligibleAdvisors 方法获取 advisor, 如果获取不到返回 DO_NOT_PROXY(不需要创建代理),findEligibleAdvisors 方法如下
/** * Find all eligible Advisors for auto-proxying this class. * @param beanClass the clazz to find advisors for * @param beanName the name of the currently proxied bean * @return the empty List, not {@code null}, * if there are no pointcuts or interceptors * @see #findCandidateAdvisors * @see #sortAdvisors * @see #extendAdvisors */protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) { // 和上文一样,获取所有切面类的切面方法生成Advisor List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors(); // 找到这些Advisor中能够应用于beanClass的Advisor List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName); // 如果需要,交给子类拓展 extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); // 对Advisor排序 if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) { eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); } return eligibleAdvisors;}获取所有切面类的切面方法生成 Advisor
/** * Find all candidate Advisors to use in auto-proxying. * @return the List of candidate Advisors */protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() { Assert.state(this.advisorRetrievalHelper != null, "No BeanFactoryAdvisorRetrievalHelper available"); return this.advisorRetrievalHelper.findAdvisorBeans();}找到这些 Advisor 中能够应用于 beanClass 的 Advisor
/** * Determine the sublist of the {@code candidateAdvisors} list * that is applicable to the given class. * @param candidateAdvisors the Advisors to evaluate * @param clazz the target class * @return sublist of Advisors that can apply to an object of the given class * (may be the incoming List as-is) */public static List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> clazz) { if (candidateAdvisors.isEmpty()) { return candidateAdvisors; } List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = new ArrayList<>(); for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) { // 通过Introduction实现的advice if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor && canApply(candidate, clazz)) { eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate); } } boolean hasIntroductions = !eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty(); for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) { if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) { // already processed continue; } // 是否能够应用于clazz的Advice if (canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)) { eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate); } } return eligibleAdvisors;}创建代理的入口方法
获取所有 advisor 后,如果有 advisor,则说明需要增强,即需要创建代理,创建代理的方法如下:
/** * Create an AOP proxy for the given bean. * @param beanClass the class of the bean * @param beanName the name of the bean * @param specificInterceptors the set of interceptors that is * specific to this bean (may be empty, but not null) * @param targetSource the TargetSource for the proxy, * already pre-configured to access the bean * @return the AOP proxy for the bean * @see #buildAdvisors */protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) { AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass); }
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory(); proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
if (proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) { // Explicit handling of JDK proxy targets (for introduction advice scenarios) if (Proxy.isProxyClass(beanClass)) { // Must allow for introductions; can't just set interfaces to the proxy's interfaces only. for (Class<?> ifc : beanClass.getInterfaces()) { proxyFactory.addInterface(ifc); } } } else { // No proxyTargetClass flag enforced, let's apply our default checks... if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) { proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true); } else { evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory); } }
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors); proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors); proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource); customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy); if (advisorsPreFiltered()) { proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true); }
// Use original ClassLoader if bean class not locally loaded in overriding class loader ClassLoader classLoader = getProxyClassLoader(); if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader && classLoader != beanClass.getClassLoader()) { classLoader = ((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).getOriginalClassLoader(); } return proxyFactory.getProxy(classLoader);}proxyFactory.getProxy(classLoader)
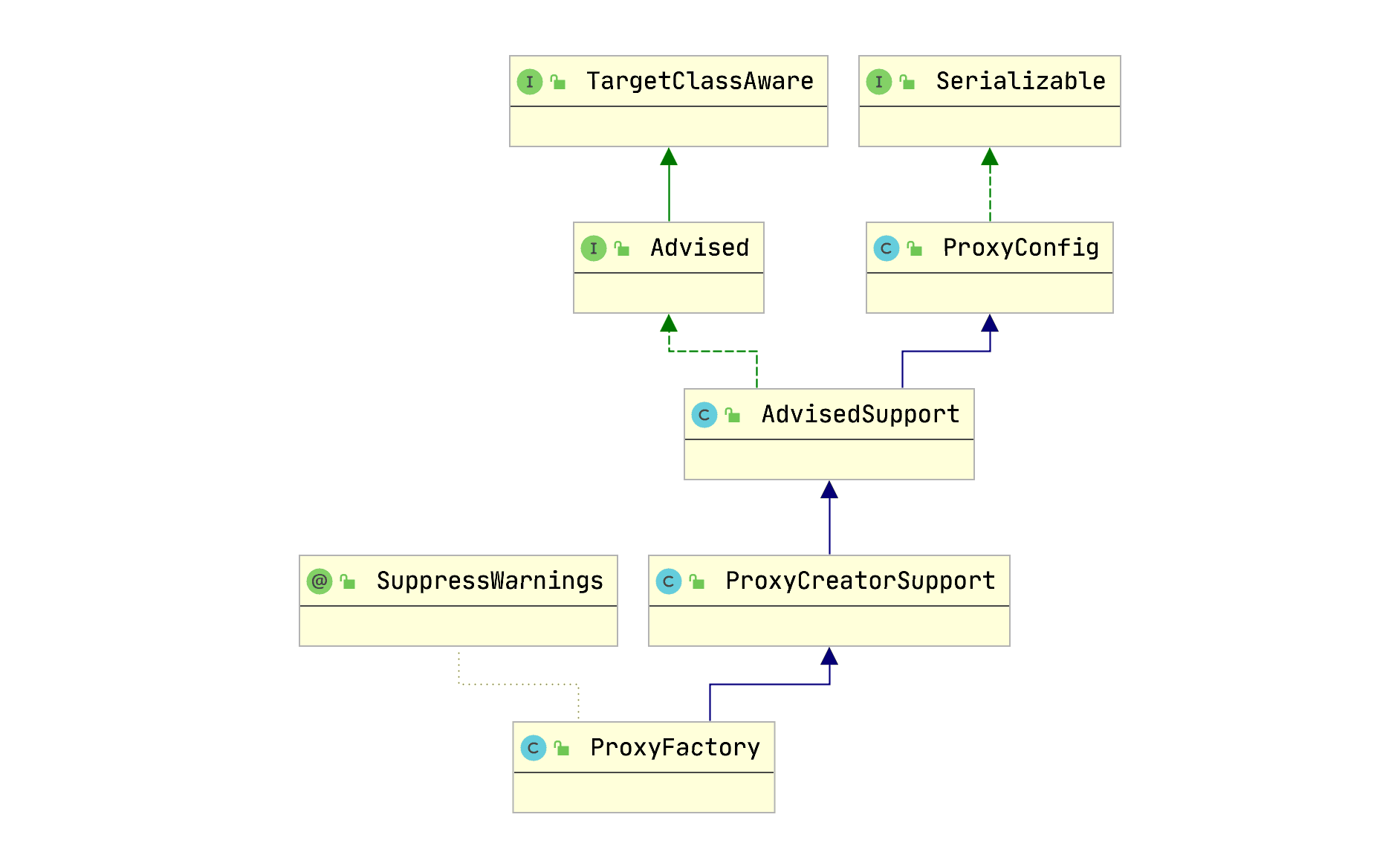
/** * Create a new proxy according to the settings in this factory. * <p>Can be called repeatedly. Effect will vary if we've added * or removed interfaces. Can add and remove interceptors. * <p>Uses the given class loader (if necessary for proxy creation). * @param classLoader the class loader to create the proxy with * (or {@code null} for the low-level proxy facility's default) * @return the proxy object */public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { return createAopProxy().getProxy(classLoader);}依据条件创建代理(jdk 或 cglib)
DefaultAopProxyFactory.createAopProxy
@Overridepublic AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException { if (!NativeDetector.inNativeImage() && (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config))) { Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass(); if (targetClass == null) { throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " + "Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation."); } if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) { return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config); } return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config); } else { return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config); }}小结
config.isOptimize() 是通过 optimize 设置,表示配置是自定义的,默认是 false;
config.isProxyTargetClass()是通过
<aop:config proxy-target-class="true" />来配置的,表示优先使用 cglib 代理,默认是 false;hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config) 表示是否目标类实现了接口
由此可以知道:
Spring 默认在目标类实现接口时是通过 JDK 代理实现的,只有非接口的是通过 Cglib 代理实现的。当设置 proxy-target-class 为 true 时在目标类不是接口或者代理类时优先使用 cglib 代理实现。
JDK 代理
JDK 动态代理是有 JDK 提供的工具类 Proxy 实现的,动态代理类是在运行时生成指定接口的代理类,每个代理实例(实现需要代理的接口)都有一个关联的调用处理程序对象,此对象实现了 InvocationHandler,最终的业务逻辑是在 InvocationHandler 实现类的 invoke 方法上。
JDK 代理的流程如下:
JDK 代理自动生成的 class 是由 sun.misc.ProxyGenerator 来生成的。
ProxyGenerator 生成代码
我们看下 sun.misc.ProxyGenerator 生成代码的逻辑:
/** * Generate a proxy class given a name and a list of proxy interfaces. * * @param name the class name of the proxy class * @param interfaces proxy interfaces * @param accessFlags access flags of the proxy class*/public static byte[] generateProxyClass(final String name, Class<?>[] interfaces, int accessFlags){ ProxyGenerator gen = new ProxyGenerator(name, interfaces, accessFlags); final byte[] classFile = gen.generateClassFile(); ...}generateClassFile 方法如下:
/** * Generate a class file for the proxy class. This method drives the * class file generation process. */private byte[] generateClassFile() {
/* 第一步:将所有方法包装成ProxyMethod对象 */ // 将Object类中hashCode、equals、toString方法包装成ProxyMethod对象 addProxyMethod(hashCodeMethod, Object.class); addProxyMethod(equalsMethod, Object.class); addProxyMethod(toStringMethod, Object.class);
// 将代理类接口方法包装成ProxyMethod对象 for (Class<?> intf : interfaces) { for (Method m : intf.getMethods()) { addProxyMethod(m, intf); } }
// 校验返回类型 for (List<ProxyMethod> sigmethods : proxyMethods.values()) { checkReturnTypes(sigmethods); }
/* 第二步:为代理类组装字段,构造函数,方法,static初始化块等 */ try { // 添加构造函数,参数是InvocationHandler methods.add(generateConstructor());
// 代理方法 for (List<ProxyMethod> sigmethods : proxyMethods.values()) { for (ProxyMethod pm : sigmethods) {
// 字段 fields.add(new FieldInfo(pm.methodFieldName, "Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;", ACC_PRIVATE | ACC_STATIC));
// 上述ProxyMethod中的方法 methods.add(pm.generateMethod()); } }
// static初始化块 methods.add(generateStaticInitializer());
} catch (IOException e) { throw new InternalError("unexpected I/O Exception", e); }
if (methods.size() > 65535) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("method limit exceeded"); } if (fields.size() > 65535) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("field limit exceeded"); }
/* 第三步:写入class文件 */
/* * Make sure that constant pool indexes are reserved for the * following items before starting to write the final class file. */ cp.getClass(dotToSlash(className)); cp.getClass(superclassName); for (Class<?> intf: interfaces) { cp.getClass(dotToSlash(intf.getName())); }
/* * Disallow new constant pool additions beyond this point, since * we are about to write the final constant pool table. */ cp.setReadOnly();
ByteArrayOutputStream bout = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); DataOutputStream dout = new DataOutputStream(bout);
try { /* * Write all the items of the "ClassFile" structure. * See JVMS section 4.1. */ // u4 magic; dout.writeInt(0xCAFEBABE); // u2 minor_version; dout.writeShort(CLASSFILE_MINOR_VERSION); // u2 major_version; dout.writeShort(CLASSFILE_MAJOR_VERSION);
cp.write(dout); // (write constant pool)
// u2 access_flags; dout.writeShort(accessFlags); // u2 this_class; dout.writeShort(cp.getClass(dotToSlash(className))); // u2 super_class; dout.writeShort(cp.getClass(superclassName));
// u2 interfaces_count; dout.writeShort(interfaces.length); // u2 interfaces[interfaces_count]; for (Class<?> intf : interfaces) { dout.writeShort(cp.getClass( dotToSlash(intf.getName()))); }
// u2 fields_count; dout.writeShort(fields.size()); // field_info fields[fields_count]; for (FieldInfo f : fields) { f.write(dout); }
// u2 methods_count; dout.writeShort(methods.size()); // method_info methods[methods_count]; for (MethodInfo m : methods) { m.write(dout); }
// u2 attributes_count; dout.writeShort(0); // (no ClassFile attributes for proxy classes)
} catch (IOException e) { throw new InternalError("unexpected I/O Exception", e); }
return bout.toByteArray();}一共三个步骤(把大象装进冰箱分几步?):
第一步:(把冰箱门打开)准备工作,将所有方法包装成 ProxyMethod 对象,包括 Object 类中 hashCode、equals、toString 方法,以及被代理的接口中的方法
第二步:(把大象装进去)为代理类组装字段,构造函数,方法,static 初始化块等
第三步:(把冰箱门带上)写入 class 文件
从生成的 Proxy 代码看执行流程
从上述 sun.misc.ProxyGenerator 类中可以看到,这个类里面有一个配置参数sun.misc.ProxyGenerator.saveGeneratedFiles,可以通过这个参数将生成的 Proxy 类保存在本地,比如设置为 true 执行后,生成的文件如下:
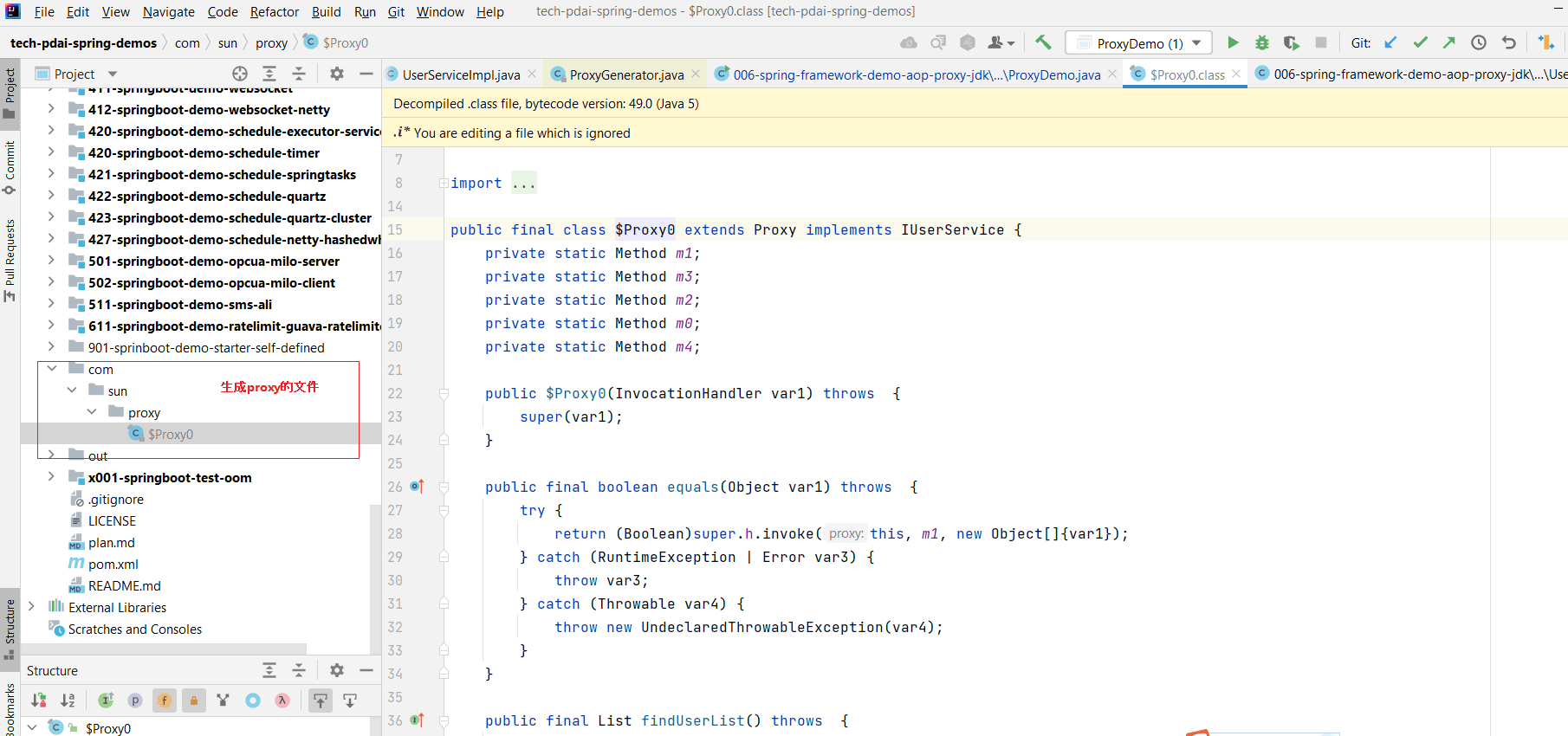
我们看下生成后的代码:
//// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)//
package com.sun.proxy;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;import java.lang.reflect.Method;import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;import java.lang.reflect.UndeclaredThrowableException;import java.util.List;import tech.pdai.springframework.service.IUserService;
// 所有类和方法都是final类型的public final class $Proxy0 extends Proxy implements IUserService { private static Method m1; private static Method m3; private static Method m2; private static Method m0; private static Method m4;
// 构造函数注入 InvocationHandler public $Proxy0(InvocationHandler var1) throws { super(var1); }
public final boolean equals(Object var1) throws { try { return (Boolean)super.h.invoke(this, m1, new Object[]{var1}); } catch (RuntimeException | Error var3) { throw var3; } catch (Throwable var4) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var4); } }
public final List findUserList() throws { try { return (List)super.h.invoke(this, m3, (Object[])null); } catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) { throw var2; } catch (Throwable var3) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3); } }
public final String toString() throws { try { return (String)super.h.invoke(this, m2, (Object[])null); } catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) { throw var2; } catch (Throwable var3) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3); } }
public final int hashCode() throws { try { return (Integer)super.h.invoke(this, m0, (Object[])null); } catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) { throw var2; } catch (Throwable var3) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3); } }
public final void addUser() throws { try { super.h.invoke(this, m4, (Object[])null); } catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) { throw var2; } catch (Throwable var3) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3); } }
static { try { // 初始化 methods, 2个IUserService接口中的方法,3个Object中的接口 m1 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("equals", Class.forName("java.lang.Object")); m3 = Class.forName("tech.pdai.springframework.service.IUserService").getMethod("findUserList"); m2 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("toString"); m0 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("hashCode"); m4 = Class.forName("tech.pdai.springframework.service.IUserService").getMethod("addUser"); } catch (NoSuchMethodException var2) { throw new NoSuchMethodError(var2.getMessage()); } catch (ClassNotFoundException var3) { throw new NoClassDefFoundError(var3.getMessage()); } }}上述代码是比较容易理解的,我就不画图了。
主要流程是:
ProxyGenerator 创建 Proxy 的具体类 $Proxy0
由 static 初始化块初始化接口方法:2 个 IUserService 接口中的方法,3 个 Object 中的接口方法
由构造函数注入 InvocationHandler
执行的时候,通过 ProxyGenerator 创建的 Proxy,调用 InvocationHandler 的 invoke 方法,执行我们自定义的 invoke 方法
SpringAOP 中 JDK 代理的实现
SpringAOP 扮演的是 JDK 代理的创建和调用两个角色,我们通过这两个方向来看下 SpringAOP 的代码(JdkDynamicAopProxy 类)
SpringAOP Jdk 代理的创建
代理的创建比较简单,调用 getProxy 方法,然后直接调用 JDK 中 Proxy.newProxyInstance()方法将 classloader 和被代理的接口方法传入即可。
@Overridepublic Object getProxy() { return getProxy(ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());}
@Overridepublic Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Creating JDK dynamic proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource()); } return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, this.proxiedInterfaces, this);}SpringAOP Jdk 代理的执行
执行的方法如下:
/** * Implementation of {@code InvocationHandler.invoke}. * <p>Callers will see exactly the exception thrown by the target, * unless a hook method throws an exception. */@Override@Nullablepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { Object oldProxy = null; boolean setProxyContext = false;
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource; Object target = null;
try { // 执行的是equal方法 if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) { // The target does not implement the equals(Object) method itself. return equals(args[0]); } // 执行的是hashcode方法 else if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) { // The target does not implement the hashCode() method itself. return hashCode(); } // 如果是包装类,则dispatch to proxy config else if (method.getDeclaringClass() == DecoratingProxy.class) { // There is only getDecoratedClass() declared -> dispatch to proxy config. return AopProxyUtils.ultimateTargetClass(this.advised); } // 用反射方式来执行切点 else if (!this.advised.opaque && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() && method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) { // Service invocations on ProxyConfig with the proxy config... return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, method, args); }
Object retVal;
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) { // Make invocation available if necessary. oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy); setProxyContext = true; }
// Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target, // in case it comes from a pool. target = targetSource.getTarget(); Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null);
// 获取拦截链 List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
// Check whether we have any advice. If we don't, we can fallback on direct // reflective invocation of the target, and avoid creating a MethodInvocation. if (chain.isEmpty()) { // We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly // Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor so we know it does // nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot swapping or fancy proxying. Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args); retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse); } else { // We need to create a method invocation... MethodInvocation invocation = new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain); // Proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain. retVal = invocation.proceed(); }
// Massage return value if necessary. Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType(); if (retVal != null && retVal == target && returnType != Object.class && returnType.isInstance(proxy) && !RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) { // Special case: it returned "this" and the return type of the method // is type-compatible. Note that we can't help if the target sets // a reference to itself in another returned object. retVal = proxy; } else if (retVal == null && returnType != Void.TYPE && returnType.isPrimitive()) { throw new AopInvocationException( "Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: " + method); } return retVal; } finally { if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) { // Must have come from TargetSource. targetSource.releaseTarget(target); } if (setProxyContext) { // Restore old proxy. AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy); } }}CGLIB 代理
代理的流程
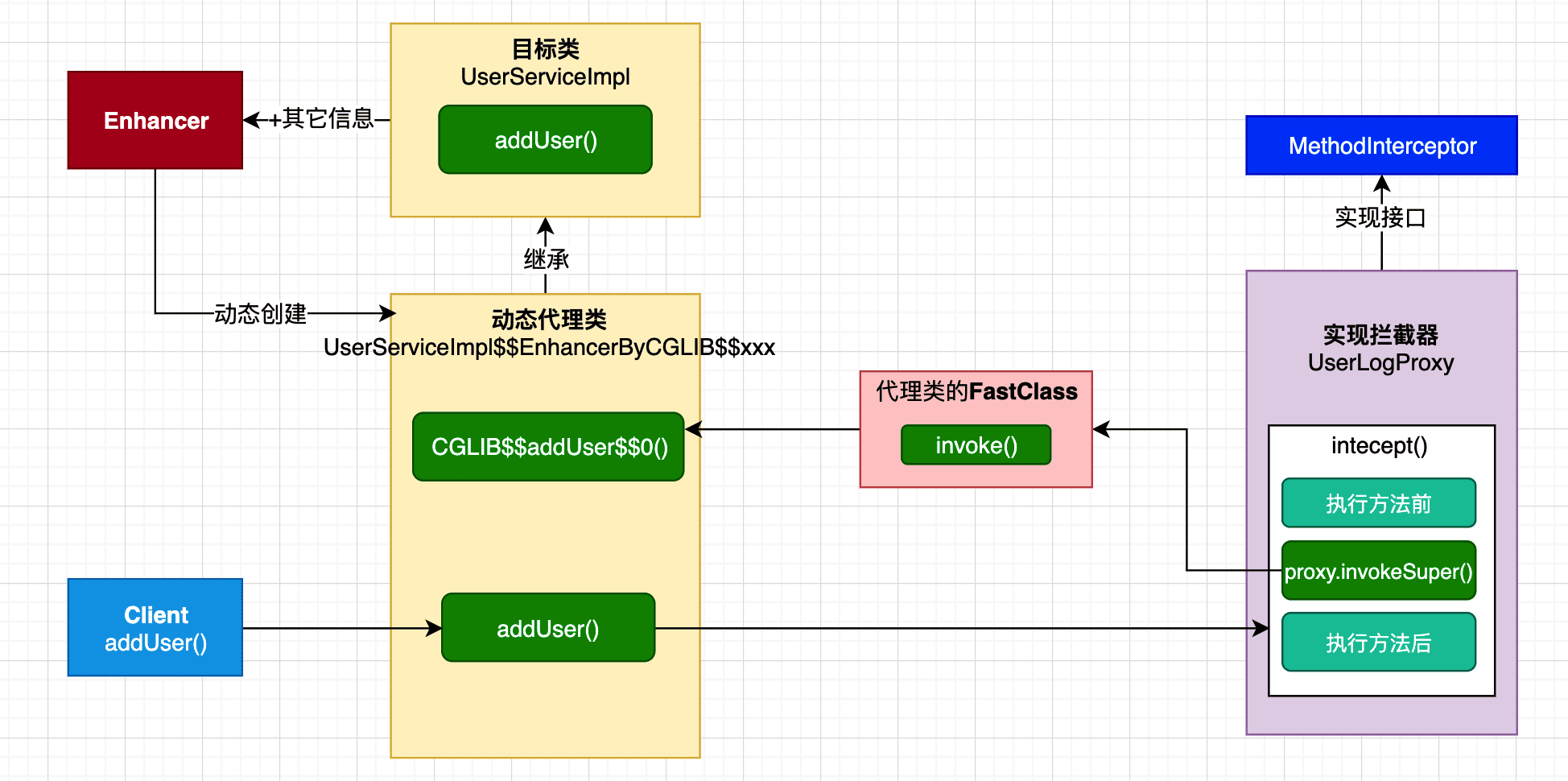
在上图中,我们可以通过在 Enhancer 中配置更多的参数来控制代理的行为,比如如果只希望增强这个类中的一个方法(而不是所有方法),那就增加 callbackFilter 来对目标类中方法进行过滤;Enhancer 可以有更多的参数类配置其行为,不过我们在学习上述主要的流程就够了。
final 方法为什么不能被代理?很显然 final 方法没法被子类覆盖,当然不能代理了。
Mockito 为什么不能 mock 静态方法?因为 mockito 也是基于 cglib 动态代理来实现的,static 方法也不能被子类覆盖,所以显然不能 mock。但 PowerMock 可以 mock 静态方法,因为它直接在 bytecode 上工作。
SpringAOP 中 Cglib 代理的实现
SpringAOP 封装了 cglib,通过其进行动态代理的创建。
我们看下 CglibAopProxy 的 getProxy 方法
@Overridepublic Object getProxy() { return getProxy(null);}
@Overridepublic Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Creating CGLIB proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource()); }
try { Class<?> rootClass = this.advised.getTargetClass(); Assert.state(rootClass != null, "Target class must be available for creating a CGLIB proxy");
// 上面流程图中的目标类 Class<?> proxySuperClass = rootClass; if (rootClass.getName().contains(ClassUtils.CGLIB_CLASS_SEPARATOR)) { proxySuperClass = rootClass.getSuperclass(); Class<?>[] additionalInterfaces = rootClass.getInterfaces(); for (Class<?> additionalInterface : additionalInterfaces) { this.advised.addInterface(additionalInterface); } }
// Validate the class, writing log messages as necessary. validateClassIfNecessary(proxySuperClass, classLoader);
// 重点看这里,就是上图的enhancer,设置各种参数来构建 Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer(); if (classLoader != null) { enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader); if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader && ((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).isClassReloadable(proxySuperClass)) { enhancer.setUseCache(false); } } enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass); enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised)); enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE); enhancer.setStrategy(new ClassLoaderAwareGeneratorStrategy(classLoader));
// 设置callback回调接口,即方法的增强点 Callback[] callbacks = getCallbacks(rootClass); Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[callbacks.length]; for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) { types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass(); } // 上节说到的filter enhancer.setCallbackFilter(new ProxyCallbackFilter( this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset)); enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types);
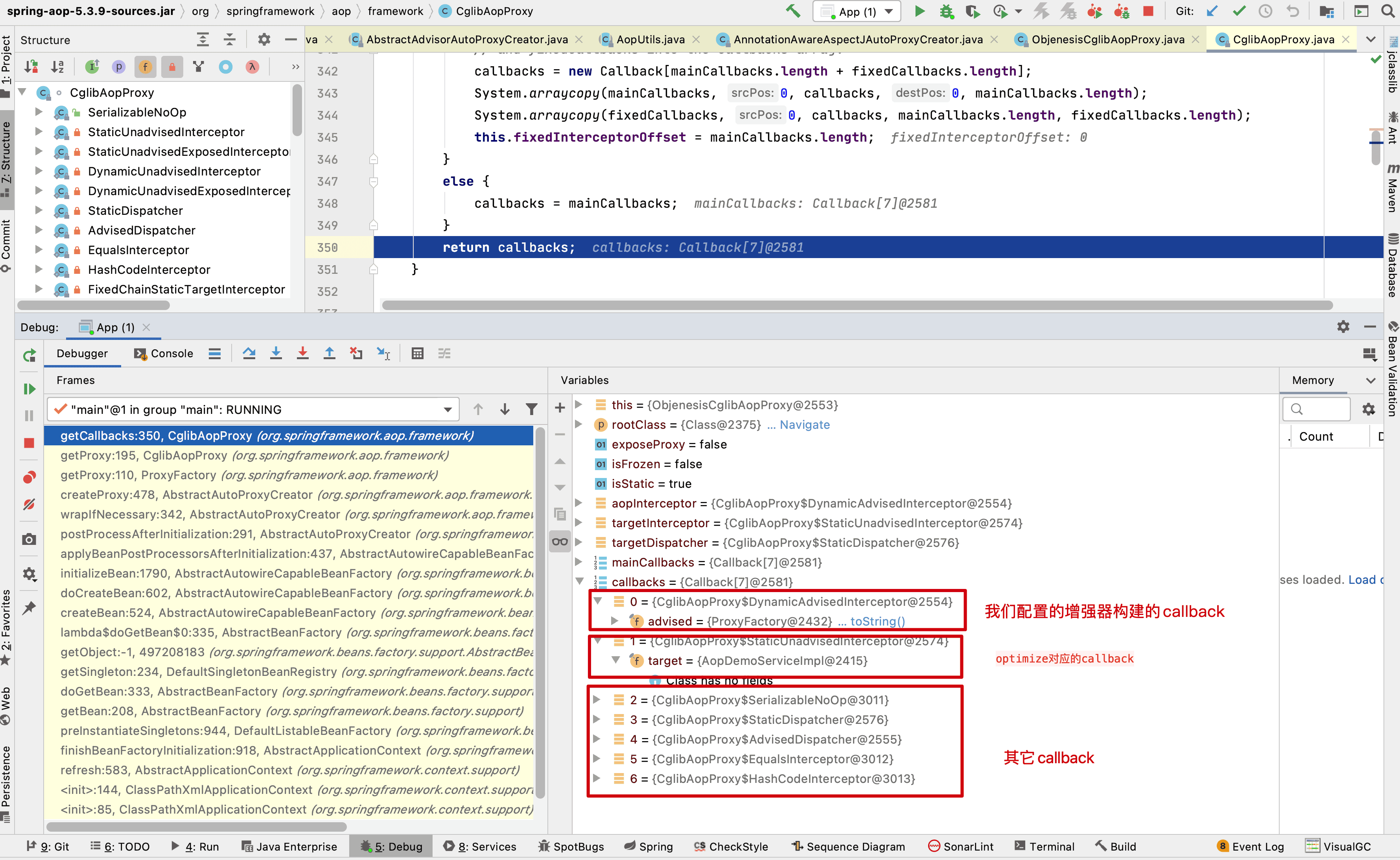
// 重点:创建proxy和其实例 return createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks); } catch (CodeGenerationException | IllegalArgumentException ex) { throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of " + this.advised.getTargetClass() + ": Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class", ex); } catch (Throwable ex) { // TargetSource.getTarget() failed throw new AopConfigException("Unexpected AOP exception", ex); }}获取 callback 的方法如下,提几个理解的要点吧,具体读者在学习的时候建议把我的例子跑一下,然后打一个断点进行理解。
rootClass: 即目标代理类advised: 包含上文中我们获取到的 advisor 增强器的集合exposeProxy: 在 xml 配置文件中配置的,背景就是如果在事务 A 中使用了代理,事务 A 调用了目标类的的方法 a,在方法 a 中又调用目标类的方法 b,方法 a,b 同时都是要被增强的方法,如果不配置 exposeProxy 属性,方法 b 的增强将会失效,如果配置 exposeProxy,方法 b 在方法 a 的执行中也会被增强了DynamicAdvisedInterceptor: 拦截器将 advised(包含上文中我们获取到的 advisor 增强器)构建配置的 AOP 的 callback(第一个 callback)targetInterceptor: xml 配置的 optimize 属性使用的(第二个 callback)最后连同其它 5 个默认的 Interceptor 返回作为 cglib 的拦截器链,之后通过 CallbackFilter 的 accpet 方法返回的索引从这个集合中返回对应的拦截增强器执行增强操作。
private Callback[] getCallbacks(Class<?> rootClass) throws Exception { // Parameters used for optimization choices... boolean exposeProxy = this.advised.isExposeProxy(); boolean isFrozen = this.advised.isFrozen(); boolean isStatic = this.advised.getTargetSource().isStatic();
// Choose an "aop" interceptor (used for AOP calls). Callback aopInterceptor = new DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(this.advised);
// Choose a "straight to target" interceptor. (used for calls that are // unadvised but can return this). May be required to expose the proxy. Callback targetInterceptor; if (exposeProxy) { targetInterceptor = (isStatic ? new StaticUnadvisedExposedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) : new DynamicUnadvisedExposedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource())); } else { targetInterceptor = (isStatic ? new StaticUnadvisedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) : new DynamicUnadvisedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource())); }
// Choose a "direct to target" dispatcher (used for // unadvised calls to static targets that cannot return this). Callback targetDispatcher = (isStatic ? new StaticDispatcher(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) : new SerializableNoOp());
Callback[] mainCallbacks = new Callback[] { aopInterceptor, // targetInterceptor, // invoke target without considering advice, if optimized new SerializableNoOp(), // no override for methods mapped to this targetDispatcher, this.advisedDispatcher, new EqualsInterceptor(this.advised), new HashCodeInterceptor(this.advised) };
Callback[] callbacks;
// If the target is a static one and the advice chain is frozen, // then we can make some optimizations by sending the AOP calls // direct to the target using the fixed chain for that method. if (isStatic && isFrozen) { Method[] methods = rootClass.getMethods(); Callback[] fixedCallbacks = new Callback[methods.length]; this.fixedInterceptorMap = CollectionUtils.newHashMap(methods.length);
// TODO: small memory optimization here (can skip creation for methods with no advice) for (int x = 0; x < methods.length; x++) { Method method = methods[x]; List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, rootClass); fixedCallbacks[x] = new FixedChainStaticTargetInterceptor( chain, this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget(), this.advised.getTargetClass()); this.fixedInterceptorMap.put(method, x); }
// Now copy both the callbacks from mainCallbacks // and fixedCallbacks into the callbacks array. callbacks = new Callback[mainCallbacks.length + fixedCallbacks.length]; System.arraycopy(mainCallbacks, 0, callbacks, 0, mainCallbacks.length); System.arraycopy(fixedCallbacks, 0, callbacks, mainCallbacks.length, fixedCallbacks.length); this.fixedInterceptorOffset = mainCallbacks.length; } else { callbacks = mainCallbacks; } return callbacks;}可以结合调试,方便理解
AOP 在嵌套方法调用时不生效
在一个实现类中,有 2 个方法,方法 A,方法 B,其中方法 B 上面有个注解切面,当方法 B 被外部调用的时候,会进入切面方法。但当方法 B 是被方法 A 调用时,并不能从方法 B 的注解上,进入到切面方法,即我们经常碰到的方法嵌套时,AOP 注解不生效的问题。
案例
外部调用 AOP 方法正常进入
通过外部,调用方法 B,可以正常进入切面方法,这个场景的代码如下:
注解类:
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)public @interface DemoAnno {
}切面类
@Aspect@Order(-1)@Componentpublic class DemoAspect {
@Before("@annotation(da)") public void beforDoSomething(JoinPoint point, DemoAnno da) throws Exception { System.out.println("before method B, print 'hello,world' " ); }}接口类
public interface DemoService { void methodDemoA();
void methodDemoB();}服务实现类
@Servicepublic class DemoServiceImpl implements DemoService { @Override public void methodDemoA(){ System.out.println("this is method A"); }
@Override @DemoAnno public void methodDemoB() { System.out.println("this is method B"); }}测试方法
@AutowiredDemoService demoService;@Testpublic void testMethod(){ demoService.methodDemoA(); demoService.methodDemoB();}输出结果:
this is method Abefore method B, print 'hello,world' this is method B方法嵌套调用,AOP 不生效
上面的代码,做下修改。在 DemoServiceImpl 实现类中,通过方法 A 去调用方法 B,然后再单元测试类中,调用方法 A。代码修改后如下:
服务实现类:
@Servicepublic class DemoServiceImpl implements DemoService { @Override public void methodDemoA(){ System.out.println("this is method A"); methodDemoB(); }
@Override @DemoAnno public void methodDemoB() { System.out.println("this is method B"); }}输出结果
this is method Athis is method B原因分析
场景 1 中,通过外部调用方法 B,是由于 spring 在启动时,根据切面类及注解,生成了 DemoService 的代理类,在调用方法 B 时,实际上是代理类先对目标方法进行了业务增强处理(执行切面类中的业务逻辑),然后再调用方法 B 本身。所以场景 1 可以正常进入切面方法;
场景 2 中,通过外部调用的是方法 A,虽然 spring 也会创建一个 cglib 的代理类去调用方法 A,但当方法 A 调用方法 B 的时候,属于类里面的内部调用,使用的是实例对象本身去去调用方法 B,非 aop 的 cglib 代理对象调用,方法 B 自然就不会进入到切面方法了。
解决方案
但实际上我们期望的是,方法 A 在调用方法 B 的时候,仍然能够进入切面方法,即需要 AOP 切面生效。这种情况下,在调用方法 B 的时候,需要使用AopContext.currentProxy()获取当前的代理对象,然后使用代理对象调用方法 B。
注:需要开启
exposeProxy=true的配置,springboot 项目中,可以在启动类上面,添加 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy(exposeProxy = true)注解。
@Servicepublic class DemoServiceImpl implements DemoService { @Override public void methodDemoA(){ System.out.println("this is method A"); DemoService service = (DemoService) AopContext.currentProxy(); service.methodDemoB(); }
@Override @DemoAnno public void methodDemoB() { System.out.println("this is method B"); }}文章转载自:Seven
EquatorCoco
还未添加个人签名 2023-06-19 加入
还未添加个人简介










评论