自动化控制 APP 不管是在工作还是生活方面,都可以帮助我们高效地完成任务,节省时间和精力。本文主要介绍自动化控制 APP 的 3 种常用方式。
1、Python + adb
这种方式需要对 Android 有一些基本的了解。adb 是一种用于调试 Android 应用程序的工具。使用 Python 和 adb 可以轻松实现自动化控制移动端 APP。
1.1、特点
这种方式最简单,但是控制效果也最粗糙。不同的手机对应的元素 x,y 轴的位置不同,所以不适合操作不同尺寸的所有手机。这种方式也只适合于开发者,对于普通用户使用成本过高。
1.2、使用步骤
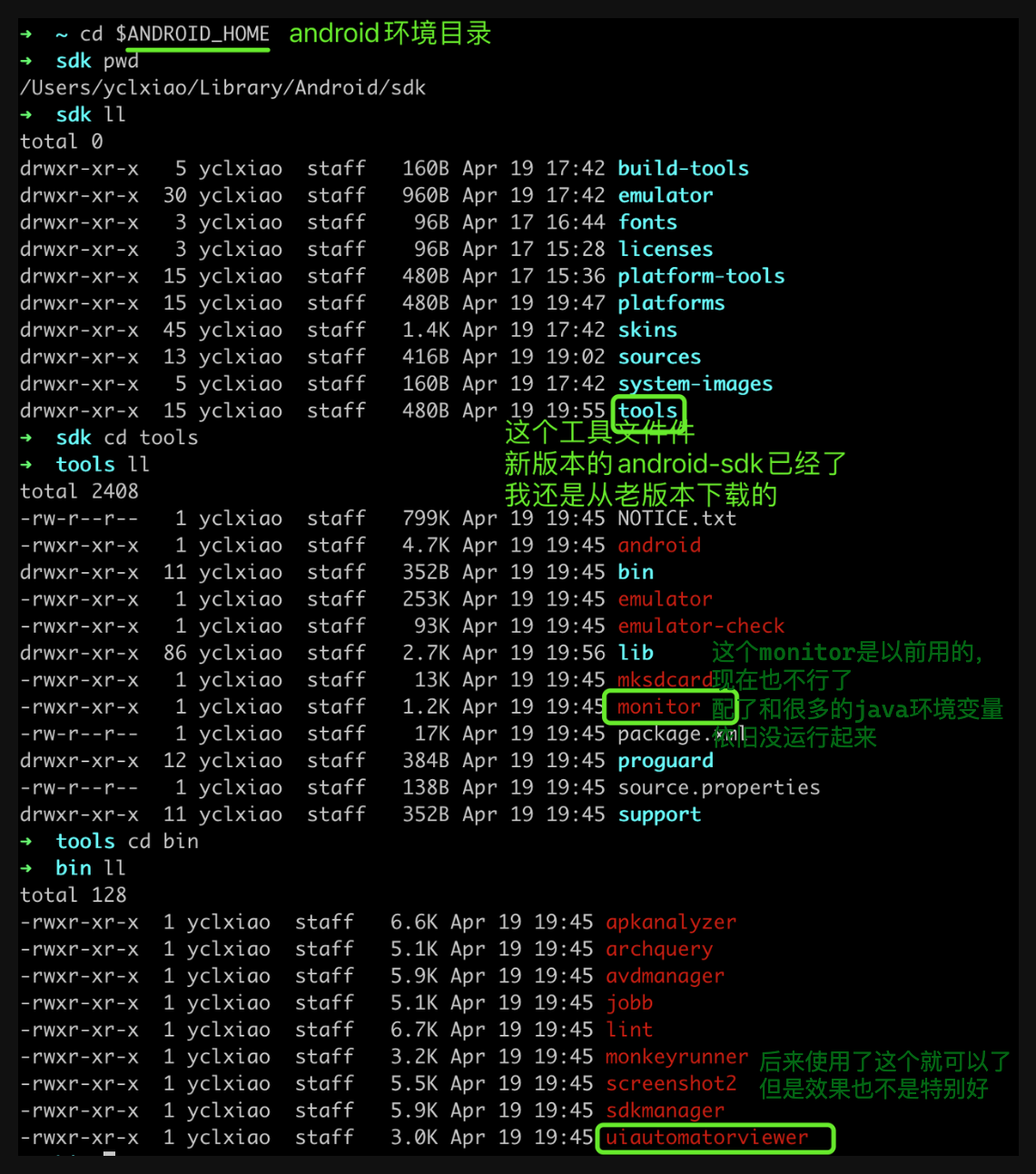
1、安装 Android SDK
具体细节略过,自行 google 安装。安装完毕后,配置好ANDROID_HOME环境变量。
2、安装 Python
具体细节略过,自行 google 安装。
3、打开手机的开发者模式
同时开启USB调试和显示指针位置。
4、此时操作手机
可以看到有 2 根轴,同时最上方会显示页面焦点元素的x,y轴位置。
5、使用 Python 代码+adb 简单控制 APP
import timeimport subprocess
# 点击某个位置subprocess.getoutput(f"adb -s Y2J7N17C27000069 shell input tap 564 1861")time.sleep(2)subprocess.getoutput(f"adb -s Y2J7N17C27000069 shell input tap 188 980")subprocess.getoutput(f"adb -s Y2J7N17C27000069 shell input tap 869 1808")time.sleep(4)subprocess.getoutput(f"adb -s Y2J7N17C27000069 shell input tap 320 965")# 输入数据subprocess.getoutput(f"adb -s Y2J7N17C27000069 shell input text 15850501595")# 按返回键subprocess.getoutput(f"adb -s Y2J7N17C27000069 shell input keyevent KEYCODE_BACK")subprocess.getoutput(f"adb -s Y2J7N17C27000069 shell input tap 512 1120")# 输入数据subprocess.getoutput(f"adb -s Y2J7N17C27000069 shell input text 15850501595")subprocess.getoutput(f"adb -s Y2J7N17C27000069 shell input keyevent KEYCODE_BACK")subprocess.getoutput(f"adb -s Y2J7N17C27000069 shell input tap 843 1824")
复制代码
6、adb 常用命令
- 查看手机设备:adb devices- 查看设备型号:adb shell getprop ro.product.model- 查看电池信息:adb shell dumpsys battery- 查看设备ID:adb shell settings get secure android_id- 查看设备IMEI:adb shell dumpsys iphonesubinfo- 查看Android版本:adb shell getprop ro.build.version.release- 查看手机网络信息:adb shell ifconfig- 查看设备日志:adb logcat- 重启手机设备:adb reboot- 安装一个apk:adb install /path/demo.apk- 卸载一个apk:adb uninstall <package>- 查看系统运行进程:adb shell ps- 查看系统磁盘情况:adb shell ls /path/- 手机设备截屏:adb shell screencap -p /sdcard/aa.png- 手机文件下载到电脑:adb pull /sdcard/aa.png ./- 电脑文件上传到手机:adb push aa.png /data/local/- 手机设备录像:adb shell screenrecord /sdcard/ab.mp4- 手机屏幕分辨率:adb shell wm size- 手机屏幕密度:adb shell wm density- 手机屏幕点击:adb -s xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx shell input tap xvalue yvalue- 手机屏幕滑动:adb shell input swipe 1000 1500 200 200- 手机屏幕带时间滑动:adb shell input swipe 1000 1500 0 0 1000- 手机文本输入:adb shell input text xxxxx- 手机键盘事件:adb shell input keyevent xxxx
复制代码
2、Android 无障碍
这种方式是使用 Android 无障碍功能实现自动控制 APP 的效果。需要开启 Android 无障碍功能,然后编写 Android 代码来控制另外的 APP 应用。
2.1、特点
这种方式需要开发者对 Android 有一些开发经验。优点是:可以用 Android 开发出独立的 apk 安装包,安装到普通用户手机里,方便用户使用。
2.2、使用步骤
1、安装 Android SDK、安装 Android Studio
具体细节略过,自行 google 安装。安装完毕后,配置好ANDROID_HOME环境变量。
2、使用 Android 自带的 tool 工具
Android 在level-21和之前的低版本,安装完毕后有一个tool工具包,但是高版本移除了此工具包。所以在安装 SDK 时还需要加上level-21版本。
使用 Android 自带的tool工具,主要是为了查看 APP 的页面布局和元素。但是monitor已经不可用了,只能使用uiAutormatorViewer。
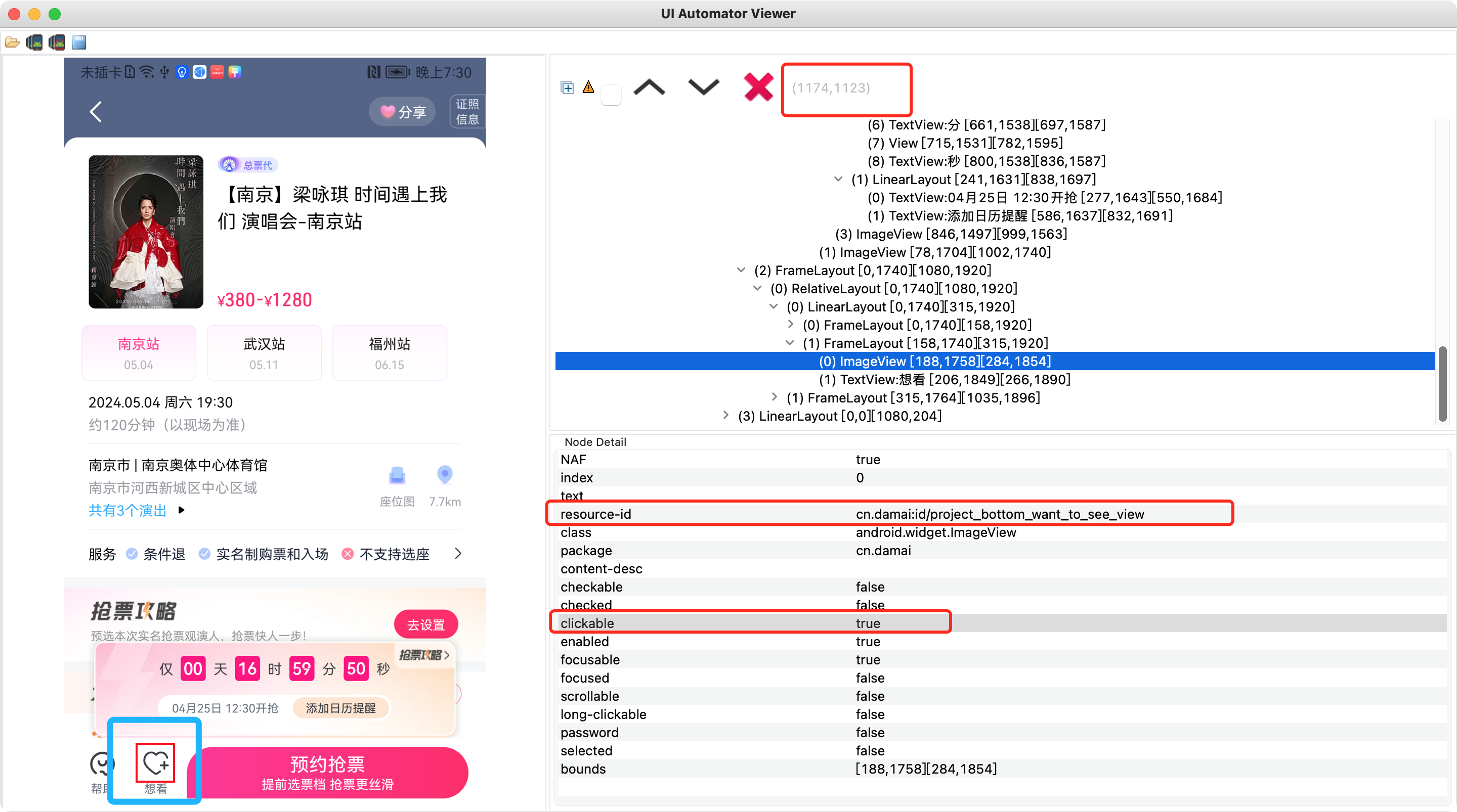
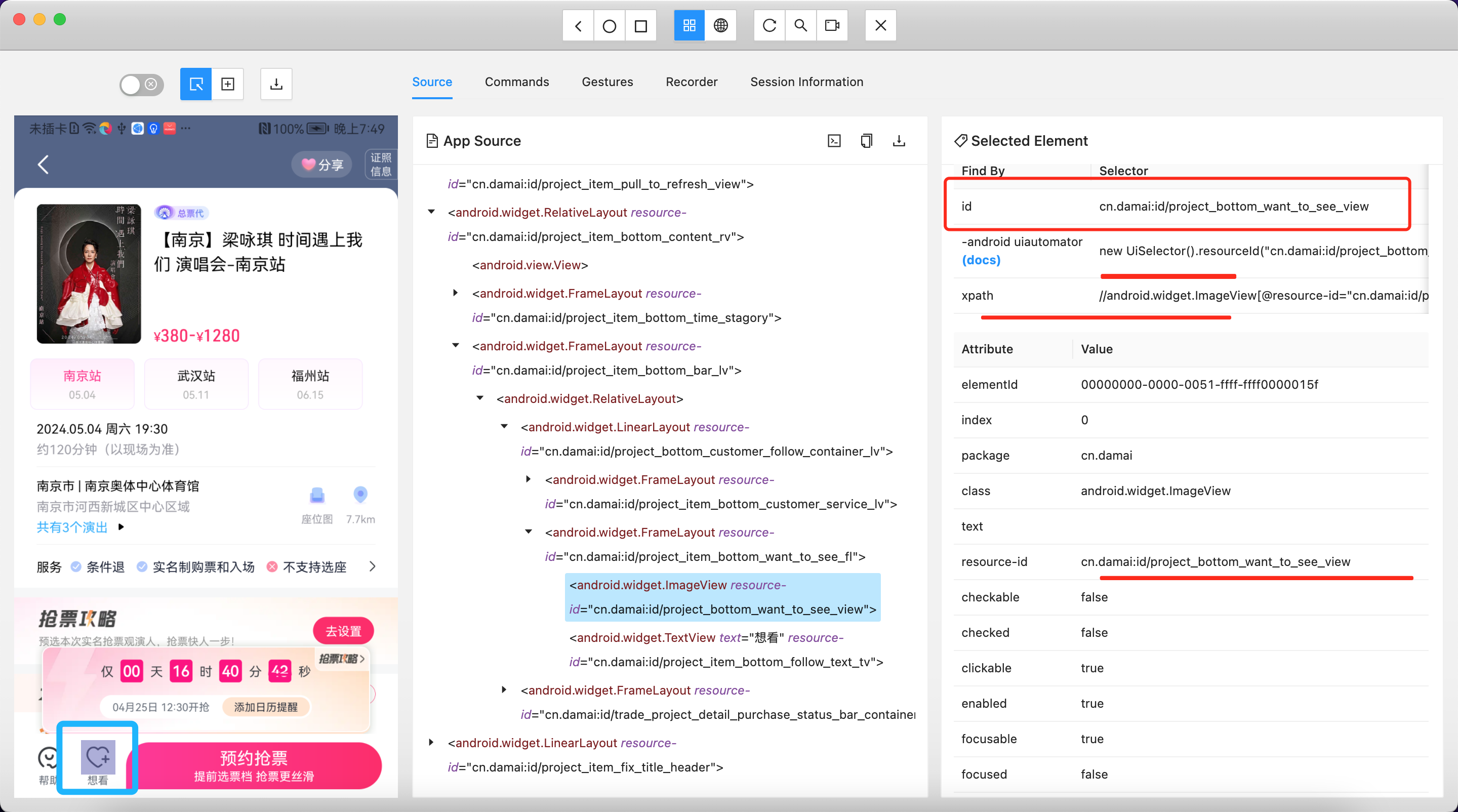
3、利用uiAutormatorViewer工具找到元素信息
用uiAutormatorViewer查看页面元素所在的x,y轴的布局。然后编写 Android 代码控制点击等效果。此工具显示出来的界面如下:
4、代码示例
在AndroidManifest.xml代码里配置无障碍 service,然后实现AccessibilityService类,实现onAccessibilityEvent方法。后续手机界面如果有变动,内部会自动触发调用onAccessibilityEvent方法。
public class XXXXXAccessibilityService extends AccessibilityService { @Override public void onInterrupt() {
}
@Override public void onAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent event) { Log.e("无障碍", "来了"); // 创建线程去执行任务 new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { // 后续代码 } }).start(); }}
复制代码
无障碍功能本身也提供了多种寻找页面元素的方法,比如:
/** * 根据ID找元素 */private AccessibilityNodeInfo findNodeById(String id) { AccessibilityNodeInfo root = getRootInActiveWindow(); if (root == null) { return null; } List<AccessibilityNodeInfo> nodeList = root.findAccessibilityNodeInfosByViewId(id); if (nodeList != null) { for (int i = 0; i < nodeList.size(); i++) { AccessibilityNodeInfo node = nodeList.get(i); if (node != null) { return node; } } } return null;}
复制代码
3、Python + Appium
Python 加 Appium 可以组合成为一种自动化测试工具,可以用于测试和自动化控制移动端 APP。
3.1、特点
这种方式可以自动化操作 APP,但是使用者基本是开发者,普通用户很难完成这一系列的操作。但是也有个优点,有些页面标记为不可点击的元素,通过这种方式是可以点击的。
Appium 提供了更多的寻找页面元素的方式,比如 uiautomator、xpath、id 等。
3.2、使用步骤
1、安装 Python
此处略过步骤,自行 google。
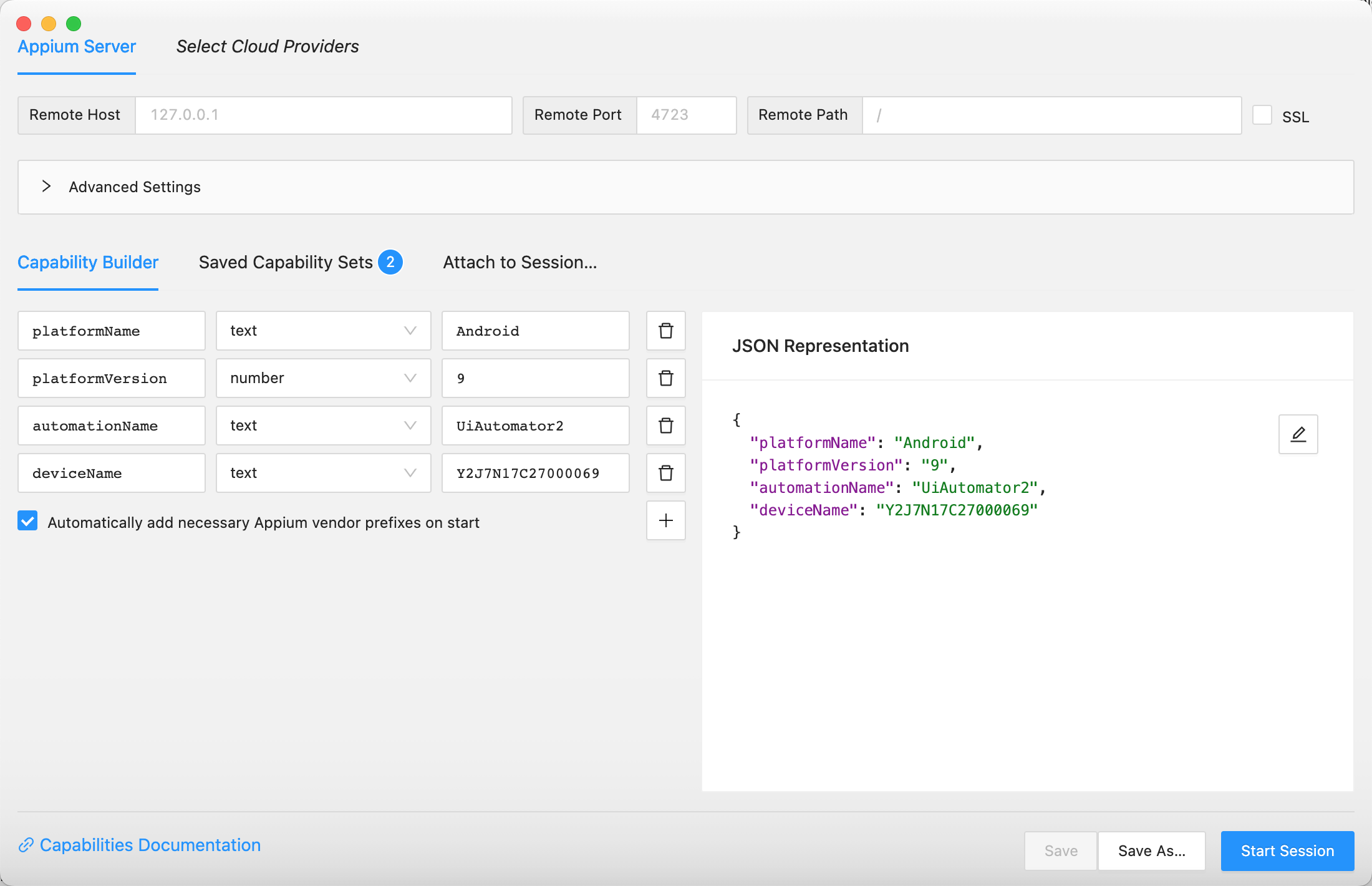
2、安装 Appium
老版本的 Appium 直接包含了Appium server 和 Appium inspector,新版本的 Appium 安装完毕后,需要在单独安装Appium inspector。通过Appium inspector可以查看手机当前页面的 xml 布局。
# 安装appiumnpm i --location=global appium
# 安装自动查看UI页面的驱动appium uiautomator2driver
# 安装inspector下载安装地址:https://github.com/appium/appium-inspector?tab=readme-ov-file
# 启动serverappium server --use-driver=uiautomator2
# 安装客户端,代码里会使用 appium-python-client 与server通信,# 然后server在将指令下发到手机里的appium端pip3 install appium-python-client
复制代码
3、使用过程
安装完毕后,就可以通过 Python 代码控制 App 了。
device_app_info = AppiumOptions()# 操作系统device_app_info.set_capability('platformName', 'Android')# 操作系统版本# device_app_info.set_capability('platformVersion', '10')device_app_info.set_capability('platformVersion', '9')# 设备名称# device_app_info.set_capability('deviceName', '46F4C19402000952')device_app_info.set_capability('deviceName', 'Y2J7N17C27000069')# app packagedevice_app_info.set_capability('appPackage', 'cn.damai')# app activity namedevice_app_info.set_capability('appActivity', '.launcher.splash.SplashMainActivity')# 使用uiautomator2驱动device_app_info.set_capability('automationName', 'UiAutomator2')
# 连接appium server,server地址查看appium启动信息driver = webdriver.Remote('http://127.0.0.1:4723', options=device_app_info)
# 找到元素,控制元素buy_btn = driver.find_element(AppiumBy.ANDROID_UIAUTOMATOR, 'new UiSelector().resourceId("cn.damai:id/trade_project_detail_purchase_status_bar_container_fl")')if buy_btn: buy_btn.click()
复制代码
4、总结
文章转载自:程序员半支烟
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/mangod/p/18156918
体验地址:http://www.jnpfsoft.com/?from=infoq








评论