基于 Redis 有序集合实现滑动窗口限流
- 2024-12-31 福建
本文字数:4949 字
阅读完需:约 16 分钟
滑动窗口算法是一种基于时间窗口的限流算法,它将时间划分为若干个固定大小的窗口,每个窗口内记录了该时间段内的请求次数。通过动态地滑动窗口,可以动态调整限流的速率,以应对不同的流量变化。
整个限流可以概括为两个主要步骤:
统计窗口内的请求数量
应用限流规则
Redis 有序集合每个 value 有一个 score(分数),基于 score 我们可以定义一个时间窗口,然后每次一个请求进来就设置一个 value,这样就可以统计窗口内的请求数量。key 可以是资源名,比如一个 url,或者 ip+url,用户标识+url 等。value 在这里不那么重要,因为我们只需要统计数量,因此 value 可以就设置成时间戳,但是如果 value 相同的话就会被覆盖,所以我们可以把请求的数据做一个 hash,将这个 hash 值当 value,或者如果每个请求有流水号的话,可以用请求流水号当 value,总之就是要能唯一标识一次请求的。
所以,简化后的命令就变成了:
ZADD 资源标识 时间戳 请求标识public boolean isAllow(String key) { ZSetOperations<String, String> zSetOperations = stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet(); // 获取当前时间戳 long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 当前时间 - 窗口大小 = 窗口开始时间 long windowStart = currentTime - period; // 删除窗口开始时间之前的所有数据 zSetOperations.removeRangeByScore(key, 0, windowStart); // 统计窗口中请求数量 Long count = zSetOperations.zCard(key); // 如果窗口中已经请求的数量超过阈值,则直接拒绝 if (count >= threshold) { return false; } // 没有超过阈值,则加入集合 String value = "请求唯一标识(比如:请求流水号、哈希值、MD5值等)"; zSetOperations.add(key, String.valueOf(currentTime), currentTime); // 设置一个过期时间,及时清理冷数据 stringRedisTemplate.expire(key, period, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); // 通过 return true;}上面代码中涉及到三条 Redis 命令,并发请求下可能存在问题,所以我们把它们写成 Lua 脚本
local key = KEYS[1]local current_time = tonumber(ARGV[1])local window_size = tonumber(ARGV[2])local threshold = tonumber(ARGV[3])redis.call('ZREMRANGEBYSCORE', key, 0, current_time - window_size)local count = redis.call('ZCARD', key)if count >= threshold then return tostring(0)else redis.call('ZADD', key, tostring(current_time), current_time) return tostring(1)end完整的代码如下:
package com.example.demo.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ZSetOperations;import org.springframework.data.redis.core.script.DefaultRedisScript;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.Collections;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/** * 基于Redis有序集合实现滑动窗口限流 * @Author: ChengJianSheng * @Date: 2024/12/26 */@Servicepublic class SlidingWindowRatelimiter {
private long period = 60*1000; // 1分钟 private int threshold = 3; // 3次
@Autowired private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
/** * RedisTemplate */ public boolean isAllow(String key) { ZSetOperations<String, String> zSetOperations = stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet(); // 获取当前时间戳 long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 当前时间 - 窗口大小 = 窗口开始时间 long windowStart = currentTime - period; // 删除窗口开始时间之前的所有数据 zSetOperations.removeRangeByScore(key, 0, windowStart); // 统计窗口中请求数量 Long count = zSetOperations.zCard(key); // 如果窗口中已经请求的数量超过阈值,则直接拒绝 if (count >= threshold) { return false; } // 没有超过阈值,则加入集合 String value = "请求唯一标识(比如:请求流水号、哈希值、MD5值等)"; zSetOperations.add(key, String.valueOf(currentTime), currentTime); // 设置一个过期时间,及时清理冷数据 stringRedisTemplate.expire(key, period, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); // 通过 return true; }
/** * Lua脚本 */ public boolean isAllow2(String key) { String luaScript = "local key = KEYS[1]\n" + "local current_time = tonumber(ARGV[1])\n" + "local window_size = tonumber(ARGV[2])\n" + "local threshold = tonumber(ARGV[3])\n" + "redis.call('ZREMRANGEBYSCORE', key, 0, current_time - window_size)\n" + "local count = redis.call('ZCARD', key)\n" + "if count >= threshold then\n" + " return tostring(0)\n" + "else\n" + " redis.call('ZADD', key, tostring(current_time), current_time)\n" + " return tostring(1)\n" + "end";
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
DefaultRedisScript<String> redisScript = new DefaultRedisScript<>(luaScript, String.class);
String result = stringRedisTemplate.execute(redisScript, Collections.singletonList(key), String.valueOf(currentTime), String.valueOf(period), String.valueOf(threshold)); // 返回1表示通过,返回0表示拒绝 return "1".equals(result); }}这里用 StringRedisTemplate 执行 Lua 脚本,先把 Lua 脚本封装成 DefaultRedisScript 对象。注意,千万注意,Lua 脚本的返回值必须是字符串,参数也最好都是字符串,用整型的话可能类型转换错误。
String requestId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
DefaultRedisScript<String> redisScript = new DefaultRedisScript<>(luaScript, String.class);
String result = stringRedisTemplate.execute(redisScript, Collections.singletonList(key), requestId, String.valueOf(period), String.valueOf(threshold));好了,上面就是基于 Redis 有序集合实现的滑动窗口限流。顺带提一句,Redis List 类型也可以用来实现滑动窗口。
接下来,我们来完善一下上面的代码,通过 AOP 来拦截请求达到限流的目的
为此,我们必须自定义注解,然后根据注解参数,来个性化的控制限流。那么,问题来了,如果获取注解参数呢?
举例说明:
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Target(ElementType.METHOD)public @interface MyAnnotation { String value();}
@Aspect@Componentpublic class MyAspect {
@Before("@annotation(myAnnotation)") public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint, MyAnnotation myAnnotation) { // 获取注解参数 String value = myAnnotation.value(); System.out.println("Annotation value: " + value);
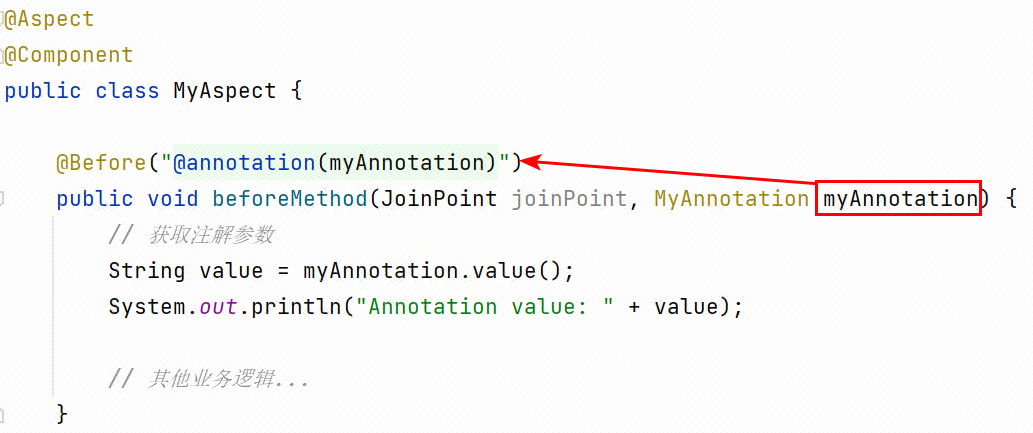
// 其他业务逻辑... }}注意看,切点是怎么写的 @Before("@annotation(myAnnotation)")
是 @Before("@annotation(myAnnotation)"),而不是 @Before("@annotation(MyAnnotation)")
myAnnotation,是参数,而 MyAnnotation 则是注解类
言归正传,我们首先定义一个注解
package com.example.demo.controller;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/** * 请求速率限制 * @Author: ChengJianSheng * @Date: 2024/12/26 */@Documented@Target(ElementType.METHOD)@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)public @interface RateLimit { /** * 窗口大小(默认:60秒) */ long period() default 60;
/** * 阈值(默认:3次) */ long threshold() default 3;}定义切面
package com.example.demo.controller;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ZSetOperations;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.RequestContextUtils;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/** * @Author: ChengJianSheng * @Date: 2024/12/26 */@Slf4j@Aspect@Componentpublic class RateLimitAspect {
@Autowired private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
// @Autowired// private SlidingWindowRatelimiter slidingWindowRatelimiter;
@Before("@annotation(rateLimit)") public void doBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint, RateLimit rateLimit) { // 获取注解参数 long period = rateLimit.period(); long threshold = rateLimit.threshold();
// 获取请求信息 ServletRequestAttributes servletRequestAttributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes(); HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest = servletRequestAttributes.getRequest(); String uri = httpServletRequest.getRequestURI(); Long userId = 123L; // 模拟获取用户ID String key = "limit:" + userId + ":" + uri; /* if (!slidingWindowRatelimiter.isAllow2(key)) { log.warn("请求超过速率限制!userId={}, uri={}", userId, uri); throw new RuntimeException("请求过于频繁!"); }*/
ZSetOperations<String, String> zSetOperations = stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet(); // 获取当前时间戳 long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 当前时间 - 窗口大小 = 窗口开始时间 long windowStart = currentTime - period * 1000; // 删除窗口开始时间之前的所有数据 zSetOperations.removeRangeByScore(key, 0, windowStart); // 统计窗口中请求数量 Long count = zSetOperations.zCard(key); // 如果窗口中已经请求的数量超过阈值,则直接拒绝 if (count < threshold) { // 没有超过阈值,则加入集合 zSetOperations.add(key, String.valueOf(currentTime), currentTime); // 设置一个过期时间,及时清理冷数据 stringRedisTemplate.expire(key, period, TimeUnit.SECONDS); } else { throw new RuntimeException("请求过于频繁!"); } }
}加注解
@RestController@RequestMapping("/hello")public class HelloController {
@RateLimit(period = 30, threshold = 2) @GetMapping("/sayHi") public void sayHi() {
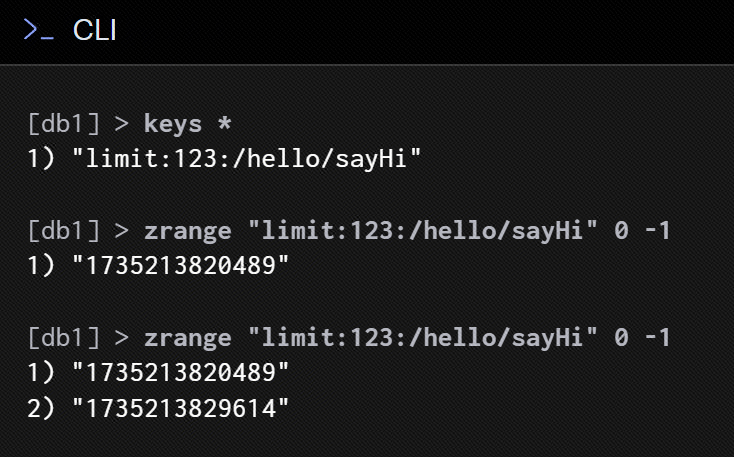
}}最后,看 Redis 中的数据结构
文章转载自:废物大师兄
快乐非自愿限量之名
还未添加个人签名 2023-06-19 加入
还未添加个人简介










评论