用 javascript 分类刷 leetcode23. 并查集 (图文视频讲解)
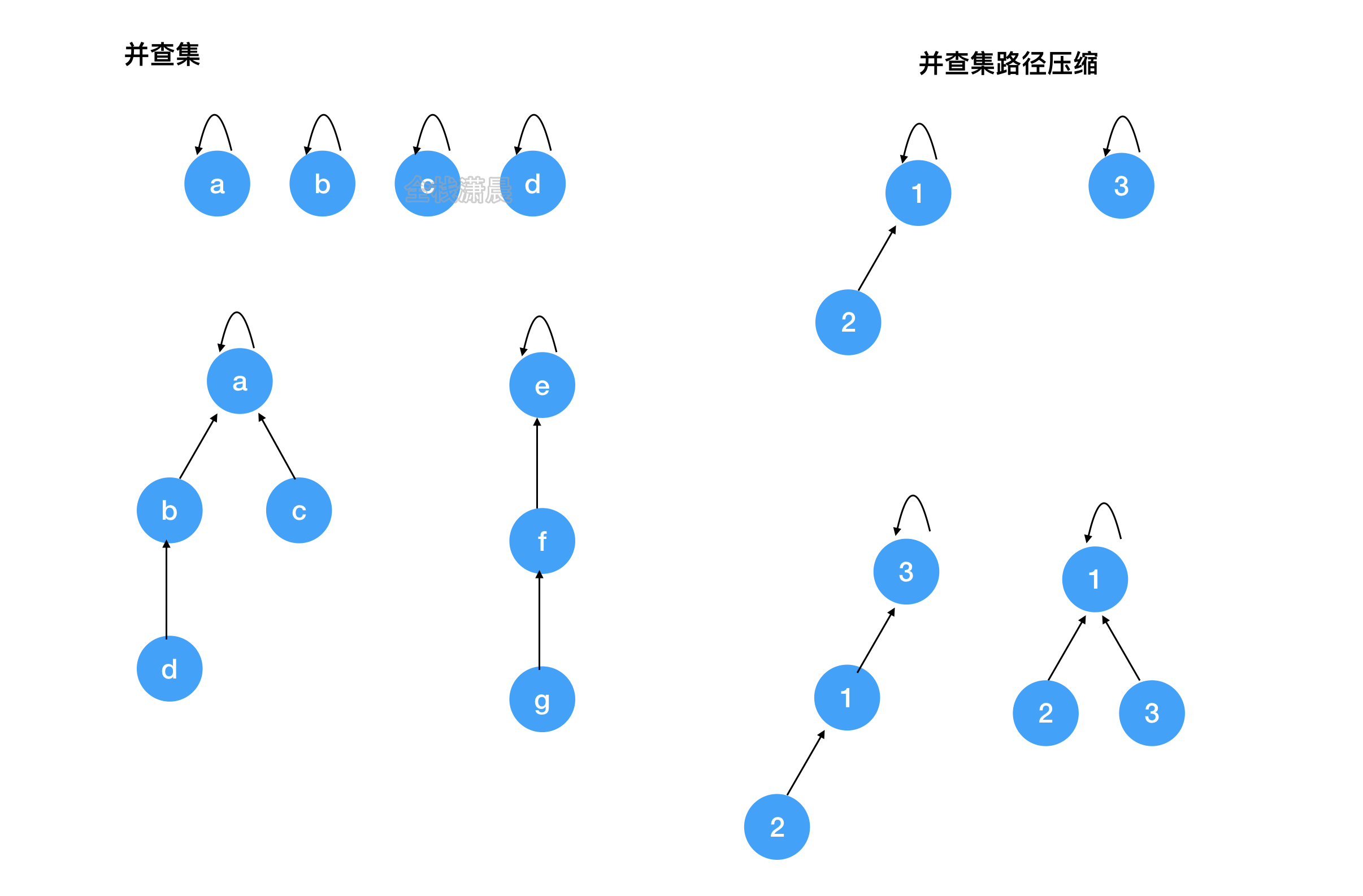
并查集(union & find):用于处理一些元素的合并和查询问题
Find:确定元素属于哪一个子集,他可以被用来确定两个元素是否属于同一个子集,加入路径压缩,复杂度近乎O(1)
Union:将两个子集合并成同一个集合
200. 岛屿数量 (medium)
给你一个由 '1'(陆地)和 '0'(水)组成的的二维网格,请你计算网格中岛屿的数量。
岛屿总是被水包围,并且每座岛屿只能由水平方向和/或竖直方向上相邻的陆地连接形成。
此外,你可以假设该网格的四条边均被水包围。
示例 1:
输入:grid = [ ["1","1","1","1","0"], ["1","1","0","1","0"], ["1","1","0","0","0"], ["0","0","0","0","0"]]输出:1 示例 2:
输入:grid = [ ["1","1","0","0","0"], ["1","1","0","0","0"], ["0","0","1","0","0"], ["0","0","0","1","1"]]输出:3
提示:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 300grid[i][j] 的值为 '0' 或 '1'
方法 1.dfs
思路:循环网格,深度优先遍历每个坐标的四周,注意坐标不要越界,遇到陆地加 1,并沉没四周的陆地,这样就不会重复计算
复杂度:时间复杂度
O(mn), m 和 n 是行数和列数。空间复杂度是O(mn),最坏的情况下所有网格都需要递归,递归栈深度达到m * n
js:
方法 2.bfs
思路:循环网格,广度优先遍历坐标的四周,遇到陆地加 1,沉没四周的陆地,不重复计算陆地数
复杂度:时间复杂度
O(mn),m 和 n 是行数和列数。空间复杂度是O(min(m,n)),队列的长度最坏的情况下需要能容得下 m 和 n 中的较小者
js:
方法 3.并查集
思路:
复杂度:时间复杂度
O(mn),时间复杂度其实是O(mn * f(mn)),f 是采用并查集路径压缩时的复杂度,为常数,所以可以忽略。 m 和 n 是行数和列数。空间复杂度是O(mn),并查集的空间
js:
547. 省份数量(medium)
有 n 个城市,其中一些彼此相连,另一些没有相连。如果城市 a 与城市 b 直接相连,且城市 b 与城市 c 直接相连,那么城市 a 与城市 c 间接相连。
省份 是一组直接或间接相连的城市,组内不含其他没有相连的城市。
给你一个 n x n 的矩阵 isConnected ,其中 isConnected[i][j] = 1 表示第 i 个城市和第 j 个城市直接相连,而 isConnected[i][j] = 0 表示二者不直接相连。
返回矩阵中 省份 的数量。
示例 1:
输入:isConnected = [[1,1,0],[1,1,0],[0,0,1]]输出:2
示例 2:
输入:isConnected = [[1,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,1]]输出:3
提示:
1 <= n <= 200n == isConnected.lengthn == isConnected[i].lengthisConnected[i][j] 为 1 或 0isConnected[i][i] == 1isConnected[i][j] == isConnected[j][i]
方法 1.dfs
思路:深度优先遍历,visited 记录是否访问过,循环省份数组,递归寻找 isConnected 矩阵中相邻的城市。
复杂度:时间复杂度
O(n^2),n 是城市的数量,遍历矩阵中的每个元素。空间复杂度O(n),递归深度不超过 n
js
方法 2.bfs
思路:广度优先遍历,循矩阵,然后寻找相邻城市加入队列,队列不为空就不断出队,继续遍历
复杂度:时间复杂度
O(n^2),n 是城市的数量,遍历矩阵中的每个元素。空间复杂度O(n),队列和 visited 数组最长是 n
js:
方法 3.并查集
思路:循环矩阵,遇到相邻的城市就合并,最后返回并查集中集合的数量
复杂度:时间复杂度
O(n^2),n 是城市的数量,需要遍历矩阵,经过路径压缩后的并查集中需找父节点复杂度是常数级。空间复杂度是O(n),即 parent 的空间
js:
视频讲解:传送门








评论