Spring 源码 -MVC 启动
加载
Servlet context listener (web.xml) approach
A web application WAR is being deployed by user.
Servlet container (Tomcat) reads
web.xml.Servlet context listener ContextLoaderListener is being instantiated (if defined as
<listener>inside theweb.xml) by servlet container.ContextLoaderListenercreates new WebApplicationContext with application context XML configuration.Your ROOT context beans are registered and instantiated byBeanFactoryinside the application context.DispatcherServlet is being instantiated by servlet container.
DispatcherServletcreates its ownWebApplicationContext(WEB-INF/{servletName}-servlet.xmlby default) with the ROOT context as its parent.Your servlet beans are registered and instantiated by BeanFactory inside the application context.DispatcherServletregisters some default beans in case you did not provide them yourself.
Servlet container initializer (non web.xml) approach
A web application WAR is being deployed by user.
Servlet container searches for classes implementing ServletContainerInitializer via Java's ServiceLoader.
Spring's SpringServletContainerInitializer is found and instantiated by servlet container.
Spring's initializer reads web application's class-path and searches for WebApplicationInitializer implementations.
Your
WebApplicationInitializeris found (btw. check its JavaDoc!!!) and instantiated bySpringServletContainerInitializer.YourWebApplicationInitializercreates new ROOT WebApplicationContext with XML or@Configurationbased configuration.YourWebApplicationInitializercreates new servlet WebApplicationContext with XML or@Configurationbased configuration.YourWebApplicationInitializercreates and registers newDispatcherServletwith the context from previous step.Servlet container finishes the web application initialization and instantiates components which were registered by their class in previous steps (none in my example).
Java based approach is much more flexible. You can leave the context creation to DispatcherServlet or even the whole instantiation of DispatcherServlet itself to servlet container (just register servlet DispatcherServlet.class instead of its instance).
源码解析
ContextLoader
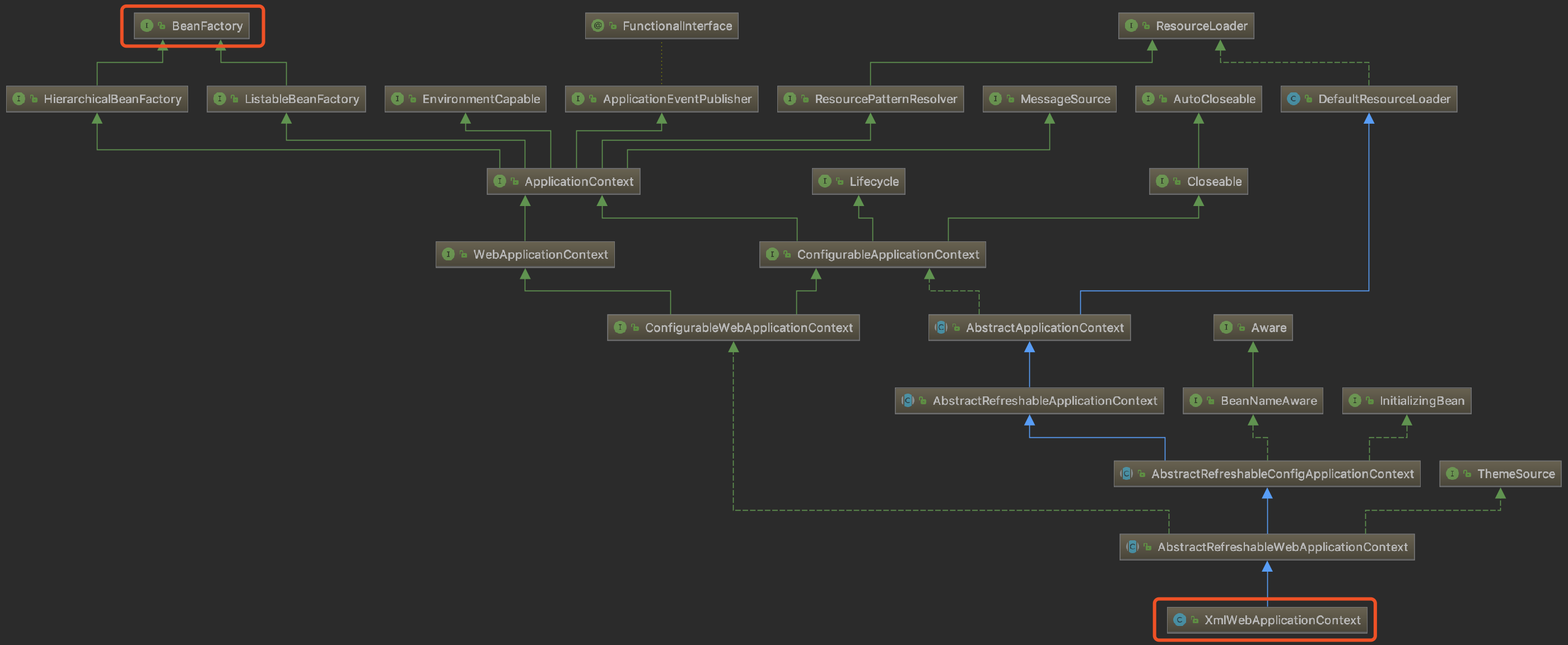
Performs the actual initialization work for the root application context.Called by ContextLoaderListener. Looks for a contextClass parameter at the web.xml context-param level to specify the context class type, falling back to XmlWebApplicationContext if not found. With the default ContextLoader implementation, any context class specified needs to implement the ConfigurableWebApplicationContext interface.
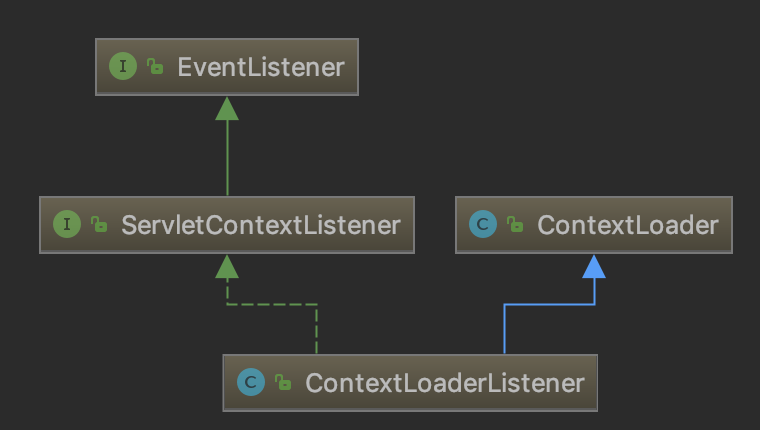
ContextLoaderListener
Bootstrap listener to start up and shut down Spring's root WebApplicationContext. Simply delegates to ContextLoader as well as to ContextCleanupListener.
ApplicationContext
Central interface to provide configuration for an application. This is read-only while the application is running, but may be reloaded if the implementation supports this.
WebApplicationContext
Interface to provide configuration for a web application. This is read-only while the application is running, but may be reloaded if the implementation supports this.
XmlWebApplicationContext
XmlWebApplicationContext implementation which takes its configuration from XML documents, understood by an XmlBeanDefinitionReader. This is essentially the equivalent of GenericXmlApplicationContext for a web environment. By default, the configuration will be taken from "/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml" for the root context.
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext
Interface to be implemented by configurable web application contexts.Supported by ContextLoader and FrameworkServlet.
java.util.EventListener
A tagging interface that all event listener interfaces must extend.
javax.servlet.ServletContextListener
Interface for receiving notification events about ServletContext lifecycle changes.
javax.servlet.ServletContext
Defines a set of methods that a servlet uses to communicate with its servlet container.
There is one context per "web application" per Java Virtual Machine. (A "web application" is a collection of servlets and content installed under a specific subset of the server's URL namespace such as /catalog and possibly installed via a *.war file.)
Web容器启动流程
当Servlet容器启动或终止Web 应用时,会触发ServletContextEvent事件,该事件由ServletContextListener来处理。ServletContextListener接口中定义了处理ServletContextEvent事件的两个方法。
Servlet API中有一个ServletContextListener接口,它能够监听ServletContext对象的生命周期,实际上就是监听 Web 应用的生命周期。









评论